Economic Outcomes
Source: Improving Quality Metrics and Reducing Cost of Care with Access to Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring, a symposium at the Academy of Managed Care Pharmacy 2021 Virtual Annual Meeting.
Featuring expert faculty:
 Jeffrey Dunn, PharmD, MBA Jeffrey Dunn, PharmD, MBAHead of Clinical Pharmacy Berkshire Hathaway/Geico (Formerly) Vice President, Clinical Strategy and Programs and Industry Relations Magellan Rx Management |  Maria Lopes, MD, MS |
 Janet B. McGill, MD, MA, FACE, FACP Janet B. McGill, MD, MA, FACE, FACPProfessor of Medicine Washington University School of Medicine |  Vanita Pindolia, PharmD, BCPS, MBA Vanita Pindolia, PharmD, BCPS, MBAVice President, Ambulatory Clinical Pharmacy Programs_PCM Henry Ford Health System/Health Alliance Plan of Michigan |
Key Takeaways:
- All insulin treated members, particularly high-risk older adults, should have streamlined access to real-time CGM, and payers should reconsider coverage criteria, such as removing intensive insulin eligibility criteria for T2D and streamlining the documentation requirements.
- Pharmacy coverage and access for appropriate subpopulations can confer immediate cost savings.
- Consensus guidelines recommend the use of rtCGM in pregnant women with pre-existing T1 and T2D and GDM. A delay in access to CGM can have adverse consequences in terms of both maternal and neonatal outcomes.
- rtCGM allows for a new frontier of diabetes management through remote monitoring and innovative patient engagement in telemedicine initiatives.
Jointly provided by Impact Education, LLC, and Medical Education Resources.
This activity is supported by an independent educational grant from Dexcom, Inc.
Source: AMCP Science and Innovation Theater Webinar – November 17, 2020
Key Takeaway: Advances in the Dexcom G6 technology are an important CGM differentiator that allows for improved safety, glycemic management and telehealth opportunities for persons 2 years and older through the use of real-time CGM data with features such as a predictive Urgent Low Soon alert, customizable high/low glycemic threshold alerts, remote monitoring and the CLARITY diabetes management application.
Learn MoreSource:
Key Takeaway: The intended place in therapy is as an alternative to routine blood glucose monitoring in people (over 2 years old), including pregnant women, with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, who use multiple daily insulin injections or use insulin pumps and are self-managing their diabetes. Dexcom G6 could reduce costs and would benefit the healthcare system by improving long-term outcomes, reducing the need for intensive treatment and, in the short term, reducing severe hypoglycaemic events leading to hospital admissions. Remote care may reduce the need for hospital visits.
Learn MoreSource:
Key Takeaway: Recent data from a prospective, randomized study conducted by Intermountain Health suggests that real-time CGM can reduce healthcare utilization and decrease the overall cost of care compared to SMBG. Participants reported that real-time CGM data were helpful in modifying their nutrition, physical activity, stress, and medication adherence.
Learn MoreSource: The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism
Key Takeaway: Nationwide reimbursement of real-time CGM improved HbA1c, fear of hypoglycemia, and QOL as well as economic indicators including work absenteeism and hospital admissions for acute diabetes complications.
The Value of rtCGM: Reduction in Hospitalizations and Work Absenteeism
| Pre-Reimbursement for rtCGM | Post-Reimbursement for rtCGM | P Value | |
| (n = 496) | (n = 379) | ||
| Patients with | |||
| Hospitalizations due to hypoglycemia and/or ketoacidosis | 77 (16%) | 14 (4%) | <0.0005 |
| Hospitalizations due to hypoglycemia | 59 (11%) | 12 (3%) | <0.0005 |
| Hospitalizations due to ketoacidosis | 23 (5%) | 4 (1%) | 0.092 |
| Work absenteesim* | 123 (25%) | 36 (9%) | <0.0005 |
| Days (per 100 patient years) of | |||
| Hospitalizations due to hypoglycemia and/or ketoacidosis | 53.5 | 17.8 | <0.0005 |
| Hospitalizations due to hypoglycemia | 38.5 | 12.5 | 0.001 |
| Hospitalizations due to ketoacidosis | 14.9 | 5.3 | 0.220 |
| Work absenteeism | 494.5 | 233.8 | 0.001 |
Data are n (%).
*Work absenteeism of at least half a day. Patient-reported hospital admissions were validated by clinicians.
Reference: Charleer S, et al. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;103(3):1224–1232
 |  |
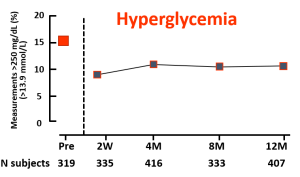 |
Reference: Charleer S, Mathieu C, Nobels F, et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;103(3):1224-1232.
LEARN MORESource: Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics
Key Takeaway: Among the real-time CGM (rtCGM) users, the change in HbA1c was greatest in the highest HbA1c subgroup with similar decreases seen in both the T1D and T2D groups. Notably, adherence remained high in those with baseline HbA1c > 9% and the improvements seen were achieved without the need for additional medications. Thus, the costs of rtCGM in patients with high HbA1c may be offset by avoiding treatment intensification and the longer-term savings achieved by lowering HbA1c levels in poorly controlled diabetes populations.
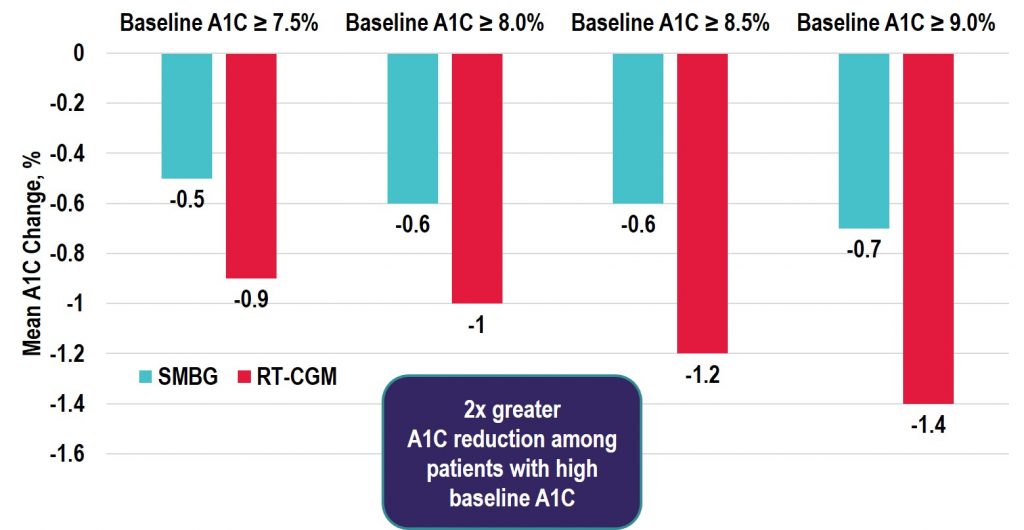
Source: Diabetes Care
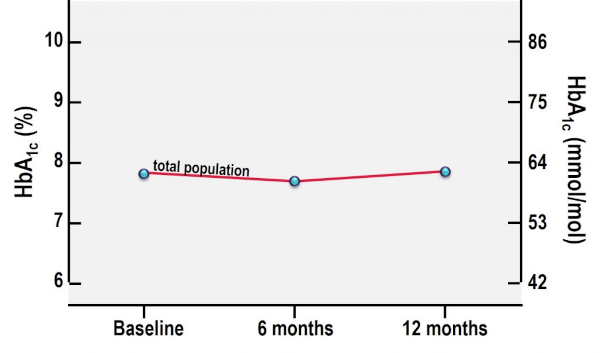
Key Takeaway: Nationwide unrestricted reimbursement of isCGM in people with type 1 diabetes treated in specialist diabetes centers results in higher treatment satisfaction, less severe hypoglycemia, and less work absenteeism, while maintaining quality of life and HbA1c.
A1C From Baseline to 12 Months After Initiation of isCGM
Source: The IQIVA Institute
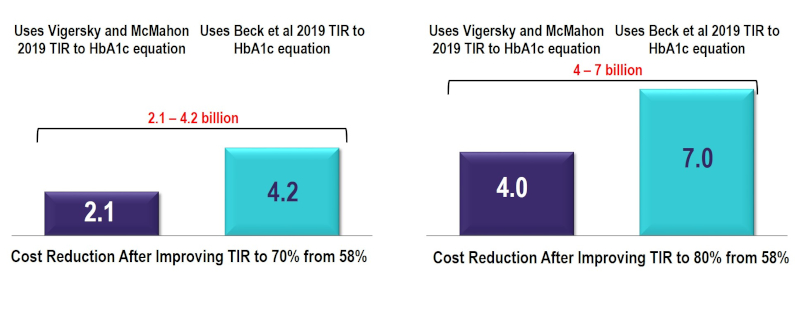
About the report: The incorporation of time in range (TIR) metrics alongside HbA1c is expected to enhance the way in which diabetes is managed in the future, and subsequently, reduce the overall societal and economic burden. To assess the value of improving TIR from its current state to the minimum consensus target of 70% and 80% TIR, the IQVIA Core Diabetes Model was used to estimate cost reductions in complications and costs associated with improving TIR. Using this model, improvements in TIR were estimated to reduce the risk of developing diabetes-related complications resulting in a conservative reduction of $2.1-7 billion in costs over a 10-year period, based on the relationship between TIR and HbA1c. The addition of incrementally reducing hypoglycemic events in people with Type 1 Diabetes by 40% and improving TIR to 80% generated a total 10-year cost reduction of $6.7-9.7 billion. This reduction in costs represents a conservative estimate.
10-Year Cost Reduction by Improving TIR in People with T1 and T2 Diabetes to 70% and 80% TIR (US$Bn)