Clinical Outcomes
Source:
Key Takeaway: In a Medicaid population of youth with Type 1 Diabetes, uninterrupted continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) use was associated with improvements in hemoglobin A1c. Interruptions in use—primarily due to gaps in insurance coverage of CGM—were associated with increased hemoglobin A1c, supporting initial and ongoing CGM coverage in high-risk, publicly insured demographics.
Learn MoreSource:
Key Takeaway: Recent data from a prospective, randomized study conducted by Intermountain Health suggests that real-time CGM can reduce healthcare utilization and decrease the overall cost of care compared to SMBG. Participants reported that real-time CGM data were helpful in modifying their nutrition, physical activity, stress, and medication adherence.
Learn MoreSource:
Key Takeaway: In a 16-week trial funded by the NIDDK and Tandem Diabetes Care, 101 children ages 6-13 with type 1 diabetes were randomized to a closed-loop system of insulin delivery (n=78) or the control group (n=23) where patients used a sensor-augmented insulin pump. Children using the closed-loop system, consisting of a t:slim X2 insulin pump with Control-IQ technology and a Dexcom G6 CGM, saw a significant time in range (TIR) improvement (target 70-180 mg/dL) from 53% at baseline to 67% (equivalent to 3.4 more hours per day; p<0.001) at the end of the study. The control group saw a smaller TIR increase from 51% at baseline to 55% at the end of the study. Notably, TIR increased most significantly overnight with children reaching 80% overnight TIR compared to 54% in the control group. The treatment effect was evident in the first month and appeared consistent over 4 months. Control-IQ technology demonstrated benefits across a broad range of baseline characteristics and proved easy to use for children and their parents.
Learn MoreSource: Journal of the American Medical Association
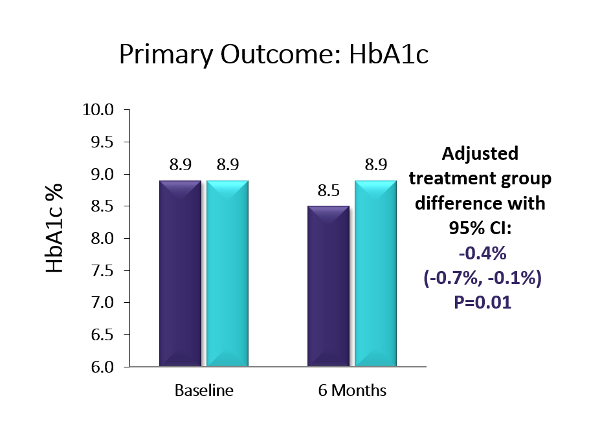
Key Takeaway: Six-month, multicenter, randomized controlled trial using the Dexcom G5. The baseline population had diverse racial/ethnic backgrounds (38% Hispanic or non-white), high baseline HbA1c levels, and 41% had public health insurance. The trial showed a 0.4% A1c advantage in favor of CGM over BGM (p=0.01; baseline: 8.9%). Moreover, more than twice as many in the CGM group as compared to the BGM group achieved an A1c reduction ≥0.5% (44% vs. 21%, p=0.005) and over four-times as many participants in the CGM group vs. the BGM group saw an A1c reduction of ≥1% (25% vs. 6%, p=0.003). The CGM group also saw a 1.7 hour/day advantage vs. BGM on time-in-range (70-180 mg/dl) (p<0.001). Over two-thirds of the CGM group were using CGM at least five days/week by the end of the six-month study – the highest CGM use observed for adolescents in a study to date. Moreover, the CGM group reported significantly higher glucose monitoring satisfaction, measured via the Glucose Monitoring Satisfaction Survey score, at 26 weeks than the BGM group . Newer models of CGM devices that eliminate fingerstick calibration should lead to improved wearability and glycemic control even beyond the measured benefits observed in this trial. Improved glycemic control early in diabetes duration may prevent diabetes complications later in adulthood, making CGM an attractive option for this population.
Source: Journal of the American Medical Association
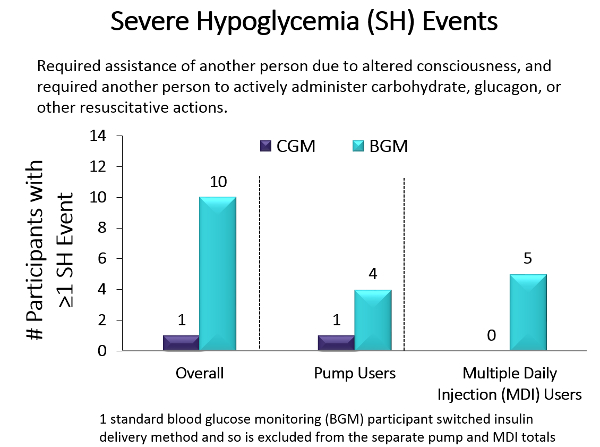
Key Takeaway: Older populations are more prone than younger populations to severe hypoglycemic episodes, which in turn contribute to dementia, risk of falls, glycemic variability, and mortality. To study whether CGM could reduce hypoglycemia incidence, Pratley and colleagues performed a randomized clinical trial that compared the effect of CGM (n = 103) with BGM (n = 100) in older adults (median age, 68 years) with type 1 diabetes in 22 diabetes centers across the US. The primary outcome was reduction in hypoglycemia (glucose <70mg/dL) over 6 months. Results showed that the median time in hypoglycemia was reduced from 73 minutes to 39 minutes per day in the CGM group compared with no change (from 68 minutes to 70 minutes per day) in the BGM group, an adjusted between group reduction of 27 minutes per day (95% CI, −40 to −16 min/d). Additionally, the median percentage of time with blood glucose levels below the range for severe hypoglycemia (glucose <54mg/dL) reached the goal per international guidelines (<14min/d in older adults). Moreover, only 1 severe hypoglycemic event (glucose <54mg/dL) occurred in the CGM group vs 10 in the BGM group, with 5 of those events involving seizure or loss of consciousness. 83% of participants in the CGM group used CGM at least 6 days per week during month 6 and the results did not differ by level of cognitive impairment, education level, or age. In summary, CGM reduced the time spent in the severe hypoglycemic range, which has health care use, mortality, morbidity, and economic benefits.
Source: Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics
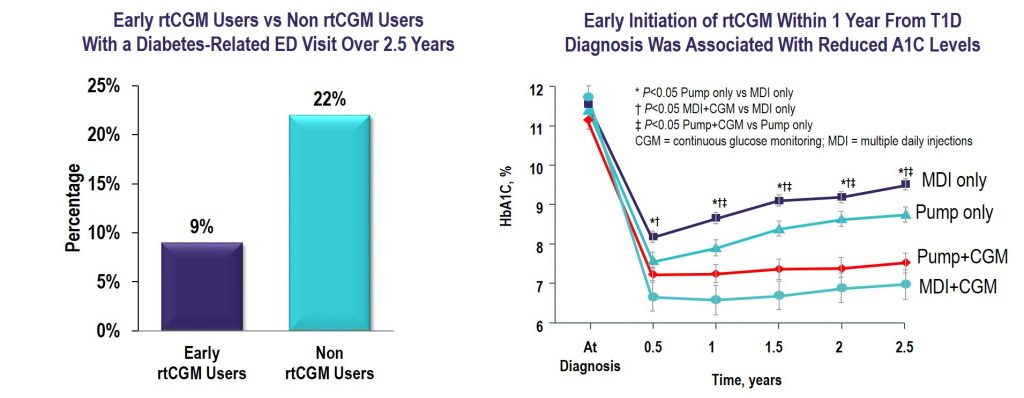
Key Takeaway: CGM initiated within the first year of T1D diagnosis was effective in lowering and maintaining A1C for 2.5 years and reduced the frequency of ED visits related to hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia irrespective of insulin delivery method.
Source: The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism
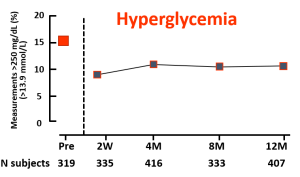
Key Takeaway: Nationwide reimbursement of real-time CGM improved HbA1c, fear of hypoglycemia, and QOL as well as economic indicators including work absenteeism and hospital admissions for acute diabetes complications.
The Value of rtCGM: Reduction in Hospitalizations and Work Absenteeism
| Pre-Reimbursement for rtCGM | Post-Reimbursement for rtCGM | P Value | |
| (n = 496) | (n = 379) | ||
| Patients with | |||
| Hospitalizations due to hypoglycemia and/or ketoacidosis | 77 (16%) | 14 (4%) | <0.0005 |
| Hospitalizations due to hypoglycemia | 59 (11%) | 12 (3%) | <0.0005 |
| Hospitalizations due to ketoacidosis | 23 (5%) | 4 (1%) | 0.092 |
| Work absenteesim* | 123 (25%) | 36 (9%) | <0.0005 |
| Days (per 100 patient years) of | |||
| Hospitalizations due to hypoglycemia and/or ketoacidosis | 53.5 | 17.8 | <0.0005 |
| Hospitalizations due to hypoglycemia | 38.5 | 12.5 | 0.001 |
| Hospitalizations due to ketoacidosis | 14.9 | 5.3 | 0.220 |
| Work absenteeism | 494.5 | 233.8 | 0.001 |
Data are n (%).
*Work absenteeism of at least half a day. Patient-reported hospital admissions were validated by clinicians.
Reference: Charleer S, et al. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;103(3):1224–1232
 |  |
 |
Reference: Charleer S, Mathieu C, Nobels F, et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;103(3):1224-1232.
LEARN MORESource: Journal of the American Medical Association
Key Takeaway: In the DIAMOND RCT, patients using multiple daily injections of insulin with type 1 diabetes who were randomly assigned to real-time CGM (rtCGM) had improved glycemic control vs. the SMBG group. This benefit was seen across patient groups regardless of baseline A1C, age, education level, or math ability. In addition, the rtCGM group spent 79% less time in nocturnal hypoglycemia, and also demonstrated a greater increase in hypoglycemic confidence and a greater decrease in diabetes distress vs. the SMBG group.
Learn MoreSource: Journal of the American Medical Association
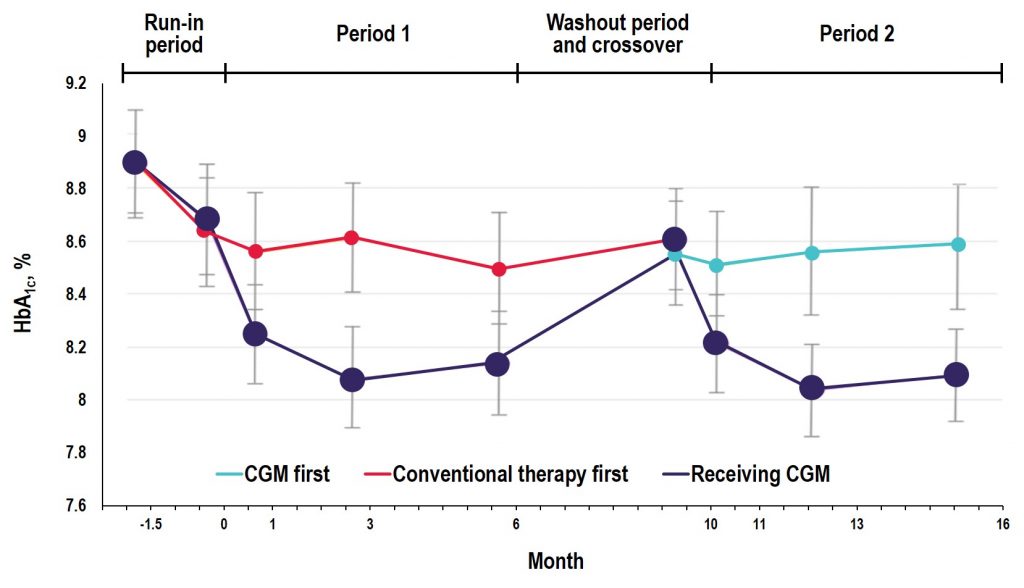
Key Takeaway: In the GOLD trial, glycemic control was improved with use of rtCGM compared with conventional treatment; however, increases in A1C and hypoglycemic events occurred when patients reverted back to SMBG during the crossover/washout period, suggesting that the effectiveness of CGM depends on uninterrupted use during treatment with MDI. Additionally, the study showed reductions in severe and nocturnal hypoglycemia as well as in glycemic variability and improved hypoglycemic confidence for rtCGM users.
Source: Diabetes Care
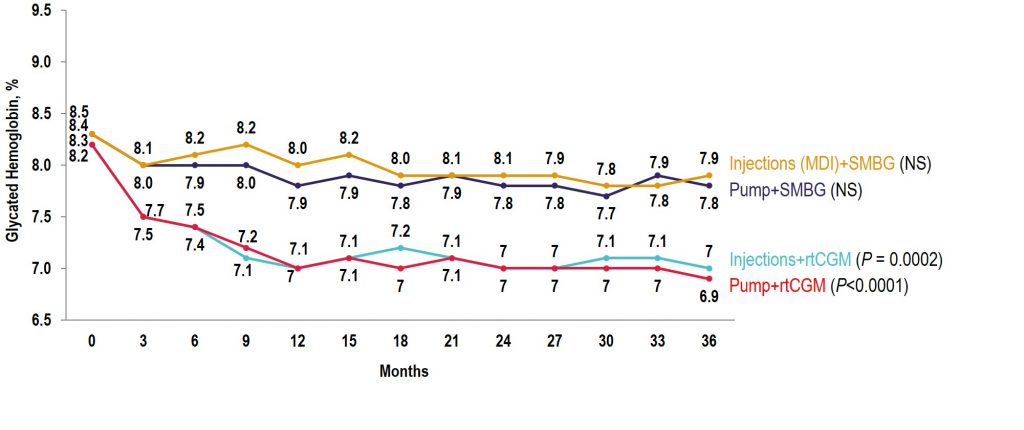
Key Takeaway: The COMISAIR study is the longest running real-world real-time CGM (rtCGM) study performed to date. In this study, the continuous use of rtCGM had a sustained and durable benefit with regards to glycemic control over a 3-year time period, with rtCGM being superior to self-monitoring of blood glucose in reducing A1C, hypoglycemia, and glycemic variability in individuals with type 1 diabetes regardless of their insulin delivery method.
Observational COMISAIR Study in Patients With T1D Who Chose Insulin Delivery Method (MDI or Pump) and Monitoring Method (SMBG or CGM), Staying on Chosen Therapy for 3 Years