Evidence
June 16, 2020Coverage and Benefit Design Article / Publication
Source: First Report Managed Care
Key Takeaway: Diabetes is a complex chronic disease that for some Type 1 and Type 2 patients requires the use of intensive insulin defined as 3 or more injections/day or insulin through a pump. The adverse consequences of using insulin are severe and can result in a coma, seizure or even death which leads many patients and caregivers deciding to use less insulin as prescribed preventing achievement of glycemic goals. Real-time CGM with alerts/alarms, remote monitoring and reporting can help patients use their insulin safely and effectively to achieve lower A1Cs, spend less time in hypo- and hyperglycemia and spend more time in range (TIR). The benefits of CGM are seen when it is used to make diabetes treatment decisions such as insulin dosing, diet and lifestyle in a timely manner. Accessing CGM devices via a pharmacy benefit allows patients to start CGM faster, stay safe while using insulin and engage pharmacists, providing additional support and interventions that have been shown to improve diabetes outcomes.
Learn More

Clinical Targets for Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data Interpretation: Recommendations From the International Consensus on Time in Range
June 16, 2020CGM Technology and Digital Health Article / Publication
Source: Diabetes Care
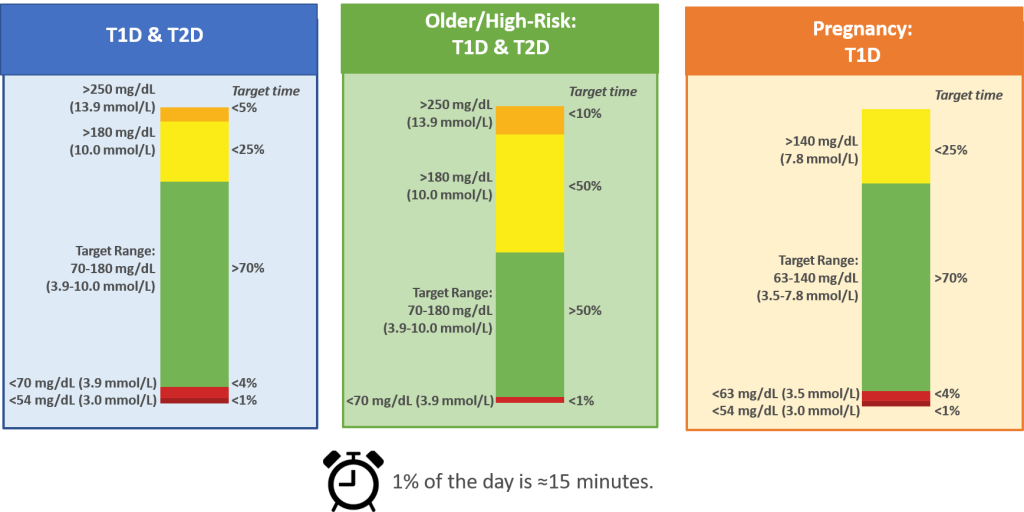
Key Takeaway: Successful utilization of CGM technology in routine clinical practice remains relatively low due to a lack of clear and agreed-upon glycemic targets that both diabetes teams and people with diabetes can work toward. In February 2019, the Advanced Technologies & Treatments for Diabetes (ATTD) Congress convened an international panel of physicians, researchers, and individuals with diabetes who are expert in CGM technologies to address this issue and established targets for time in range (TIR), time below range (TBR) and time above range (TAR). These are metrics that only CGM can measure and overcome the limitations of metrics such as A1C which are reflective of a 3 month average of glycosylated hemoglobin and does not account for day to day glycemic variability or factors such as anemia which can skew A1C low.
CGM-based Targets for Different Diabetes Populations



Glycemic Outcomes with Early Initiation of Continuous Glucose Monitoring System in Recently Diagnosed Patients with Type 1 Diabetes
June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics
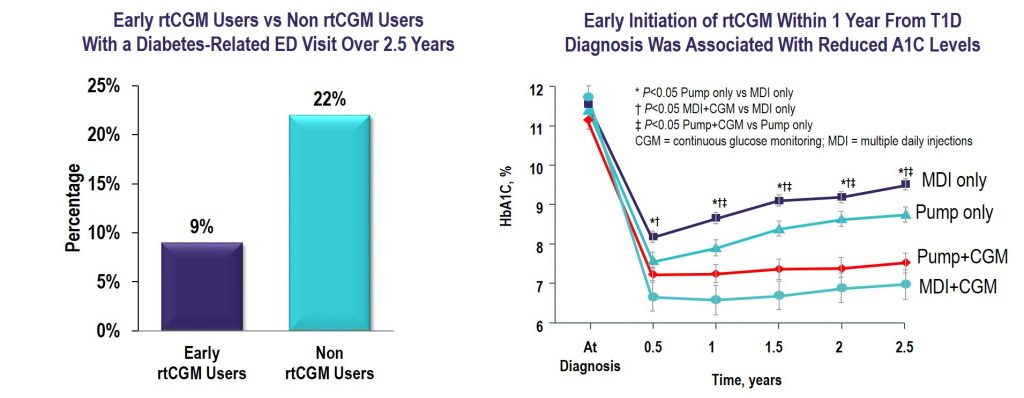
Key Takeaway: CGM initiated within the first year of T1D diagnosis was effective in lowering and maintaining A1C for 2.5 years and reduced the frequency of ED visits related to hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia irrespective of insulin delivery method.



Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Glycemic Control, Acute Admissions, and Quality of Life: A Real-World Study
June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Economic Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism
Key Takeaway: Nationwide reimbursement of real-time CGM improved HbA1c, fear of hypoglycemia, and QOL as well as economic indicators including work absenteeism and hospital admissions for acute diabetes complications.
The Value of rtCGM: Reduction in Hospitalizations and Work Absenteeism
Pre-Reimbursement for rtCGM Post-Reimbursement for rtCGM P Value (n = 496) (n = 379) Patients with Hospitalizations due to hypoglycemia and/or ketoacidosis 77 (16%) 14 (4%) <0.0005 Hospitalizations due to hypoglycemia 59 (11%) 12 (3%) <0.0005 Hospitalizations due to ketoacidosis 23 (5%) 4 (1%) 0.092 Work absenteesim* 123 (25%) 36 (9%) <0.0005 Days (per 100 patient years) of Hospitalizations due to hypoglycemia and/or ketoacidosis 53.5 17.8 <0.0005 Hospitalizations due to hypoglycemia 38.5 12.5 0.001 Hospitalizations due to ketoacidosis 14.9 5.3 0.220 Work absenteeism 494.5 233.8 0.001
Data are n (%).
*Work absenteeism of at least half a day. Patient-reported hospital admissions were validated by clinicians.
Reference: Charleer S, et al. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;103(3):1224–1232



Reference: Charleer S, Mathieu C, Nobels F, et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;103(3):1224-1232.
LEARN MORE

Real Time CGM Studies: Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Glycemic Control in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Using Insulin Injections – The DIAMOND Randomized Clinical Trial
June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Journal of the American Medical Association
Key Takeaway: In the DIAMOND RCT, patients using multiple daily injections of insulin with type 1 diabetes who were randomly assigned to real-time CGM (rtCGM) had improved glycemic control vs. the SMBG group. This benefit was seen across patient groups regardless of baseline A1C, age, education level, or math ability. In addition, the rtCGM group spent 79% less time in nocturnal hypoglycemia, and also demonstrated a greater increase in hypoglycemic confidence and a greater decrease in diabetes distress vs. the SMBG group.
Learn More

Baseline Glycated Hemoglobin Values Predict the Magnitude of Glycemic Improvement in Patients with Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes: Subgroup Analyses from the DIAMOND Study Program
June 16, 2020Economic Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics
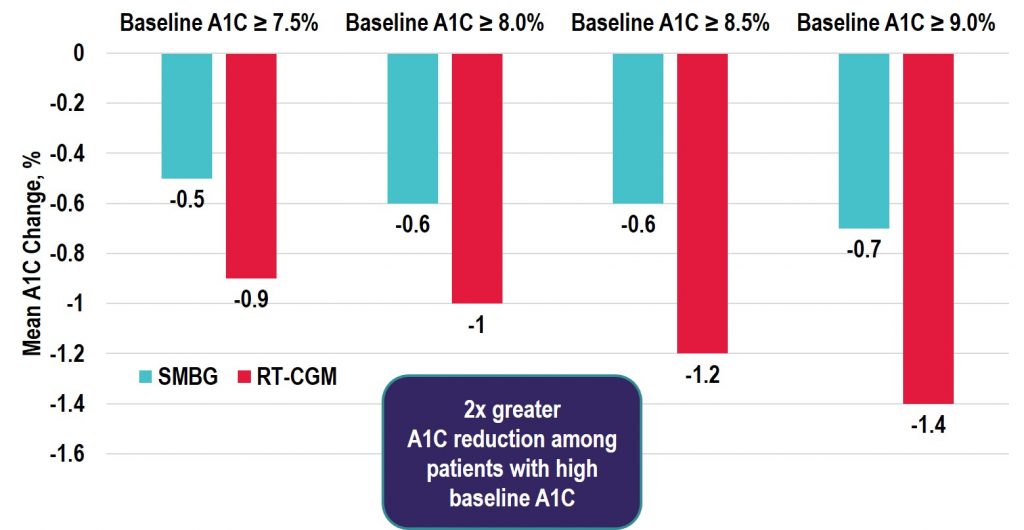
Key Takeaway: Among the real-time CGM (rtCGM) users, the change in HbA1c was greatest in the highest HbA1c subgroup with similar decreases seen in both the T1D and T2D groups. Notably, adherence remained high in those with baseline HbA1c > 9% and the improvements seen were achieved without the need for additional medications. Thus, the costs of rtCGM in patients with high HbA1c may be offset by avoiding treatment intensification and the longer-term savings achieved by lowering HbA1c levels in poorly controlled diabetes populations.



Continuous Glucose Monitoring vs Conventional Therapy for Glycemic Control in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Treated with Multiple Daily Insulin Injections – The GOLD Randomized Clinical Trial
June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Journal of the American Medical Association
Key Takeaway: In the GOLD trial, glycemic control was improved with use of rtCGM compared with conventional treatment; however, increases in A1C and hypoglycemic events occurred when patients reverted back to SMBG during the crossover/washout period, suggesting that the effectiveness of CGM depends on uninterrupted use during treatment with MDI. Additionally, the study showed reductions in severe and nocturnal hypoglycemia as well as in glycemic variability and improved hypoglycemic confidence for rtCGM users.



Glycemic Outcomes in Adults With T1D Are Impacted More by Continuous Glucose Monitoring Than by Insulin Delivery Method: 3 Years of Follow-Up From the COMISAIR Study
June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Diabetes Care
Key Takeaway: The COMISAIR study is the longest running real-world real-time CGM (rtCGM) study performed to date. In this study, the continuous use of rtCGM had a sustained and durable benefit with regards to glycemic control over a 3-year time period, with rtCGM being superior to self-monitoring of blood glucose in reducing A1C, hypoglycemia, and glycemic variability in individuals with type 1 diabetes regardless of their insulin delivery method.
Observational COMISAIR Study in Patients With T1D Who Chose Insulin Delivery Method (MDI or Pump) and Monitoring Method (SMBG or CGM), Staying on Chosen Therapy for 3 Years

June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: The New England Journal of Medicine
Key Takeaway: This 6 month randomized trial showed use of a closed-loop system using the t:slim X2 insulin pump with Control-IQ Technology, (Tandem Diabetes Care) and a continuous glucose monitor (Dexcom G6, Dexcom) was safe and effective compared to sensor-augmented pump therapy (SAP). Participants in the closed-loop group achieved 70% time in range overall which meets the International Consensus Guidelines for people with diabetes. The closed-loop group also achieved significant improvements in hyperglycemia, HbA1c, mean glucose, and hypoglycemia (< 70 mg/dL < 54 mg/dL) as compared with the SAP group. Glycemic benefits were seen in the first month of the trial and were sustained over the entire 6-month period. Over 90% of participants said they trusted the device and found Control-IQ technology easy to use.
*Full article available for a fee
Learn More

Intermittently Scanned CGM: Novel Glucose-sensing Technology and Hypoglycaemia in Type 1 Diabetes: A Multicentre, Non-masked, Randomised Controlled Trial
June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: The Lancet
Key Takeaway: This study conducted in Europe with over 300 participants found novel flash glucose testing reduced the time adults with well controlled type 1 diabetes spent in hypoglycaemia. Future studies are needed to assess the effectiveness of this technology in patients with less well controlled diabetes and in younger age groups.
Learn More
Sign Up To Stay Current On The Latest Coverage
Updates, Recent News, And Resources
Source: First Report Managed Care
Key Takeaway: Diabetes is a complex chronic disease that for some Type 1 and Type 2 patients requires the use of intensive insulin defined as 3 or more injections/day or insulin through a pump. The adverse consequences of using insulin are severe and can result in a coma, seizure or even death which leads many patients and caregivers deciding to use less insulin as prescribed preventing achievement of glycemic goals. Real-time CGM with alerts/alarms, remote monitoring and reporting can help patients use their insulin safely and effectively to achieve lower A1Cs, spend less time in hypo- and hyperglycemia and spend more time in range (TIR). The benefits of CGM are seen when it is used to make diabetes treatment decisions such as insulin dosing, diet and lifestyle in a timely manner. Accessing CGM devices via a pharmacy benefit allows patients to start CGM faster, stay safe while using insulin and engage pharmacists, providing additional support and interventions that have been shown to improve diabetes outcomes.
Learn More

Clinical Targets for Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data Interpretation: Recommendations From the International Consensus on Time in Range
June 16, 2020CGM Technology and Digital Health Article / Publication
Source: Diabetes Care
Key Takeaway: Successful utilization of CGM technology in routine clinical practice remains relatively low due to a lack of clear and agreed-upon glycemic targets that both diabetes teams and people with diabetes can work toward. In February 2019, the Advanced Technologies & Treatments for Diabetes (ATTD) Congress convened an international panel of physicians, researchers, and individuals with diabetes who are expert in CGM technologies to address this issue and established targets for time in range (TIR), time below range (TBR) and time above range (TAR). These are metrics that only CGM can measure and overcome the limitations of metrics such as A1C which are reflective of a 3 month average of glycosylated hemoglobin and does not account for day to day glycemic variability or factors such as anemia which can skew A1C low.
CGM-based Targets for Different Diabetes Populations



Glycemic Outcomes with Early Initiation of Continuous Glucose Monitoring System in Recently Diagnosed Patients with Type 1 Diabetes
June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics
Key Takeaway: CGM initiated within the first year of T1D diagnosis was effective in lowering and maintaining A1C for 2.5 years and reduced the frequency of ED visits related to hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia irrespective of insulin delivery method.



Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Glycemic Control, Acute Admissions, and Quality of Life: A Real-World Study
June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Economic Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism
Key Takeaway: Nationwide reimbursement of real-time CGM improved HbA1c, fear of hypoglycemia, and QOL as well as economic indicators including work absenteeism and hospital admissions for acute diabetes complications.
The Value of rtCGM: Reduction in Hospitalizations and Work Absenteeism
Pre-Reimbursement for rtCGM Post-Reimbursement for rtCGM P Value (n = 496) (n = 379) Patients with Hospitalizations due to hypoglycemia and/or ketoacidosis 77 (16%) 14 (4%) <0.0005 Hospitalizations due to hypoglycemia 59 (11%) 12 (3%) <0.0005 Hospitalizations due to ketoacidosis 23 (5%) 4 (1%) 0.092 Work absenteesim* 123 (25%) 36 (9%) <0.0005 Days (per 100 patient years) of Hospitalizations due to hypoglycemia and/or ketoacidosis 53.5 17.8 <0.0005 Hospitalizations due to hypoglycemia 38.5 12.5 0.001 Hospitalizations due to ketoacidosis 14.9 5.3 0.220 Work absenteeism 494.5 233.8 0.001
Data are n (%).
*Work absenteeism of at least half a day. Patient-reported hospital admissions were validated by clinicians.
Reference: Charleer S, et al. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;103(3):1224–1232



Reference: Charleer S, Mathieu C, Nobels F, et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;103(3):1224-1232.
LEARN MORE

Real Time CGM Studies: Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Glycemic Control in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Using Insulin Injections – The DIAMOND Randomized Clinical Trial
June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Journal of the American Medical Association
Key Takeaway: In the DIAMOND RCT, patients using multiple daily injections of insulin with type 1 diabetes who were randomly assigned to real-time CGM (rtCGM) had improved glycemic control vs. the SMBG group. This benefit was seen across patient groups regardless of baseline A1C, age, education level, or math ability. In addition, the rtCGM group spent 79% less time in nocturnal hypoglycemia, and also demonstrated a greater increase in hypoglycemic confidence and a greater decrease in diabetes distress vs. the SMBG group.
Learn More

Baseline Glycated Hemoglobin Values Predict the Magnitude of Glycemic Improvement in Patients with Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes: Subgroup Analyses from the DIAMOND Study Program
June 16, 2020Economic Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics
Key Takeaway: Among the real-time CGM (rtCGM) users, the change in HbA1c was greatest in the highest HbA1c subgroup with similar decreases seen in both the T1D and T2D groups. Notably, adherence remained high in those with baseline HbA1c > 9% and the improvements seen were achieved without the need for additional medications. Thus, the costs of rtCGM in patients with high HbA1c may be offset by avoiding treatment intensification and the longer-term savings achieved by lowering HbA1c levels in poorly controlled diabetes populations.



Continuous Glucose Monitoring vs Conventional Therapy for Glycemic Control in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Treated with Multiple Daily Insulin Injections – The GOLD Randomized Clinical Trial
June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Journal of the American Medical Association
Key Takeaway: In the GOLD trial, glycemic control was improved with use of rtCGM compared with conventional treatment; however, increases in A1C and hypoglycemic events occurred when patients reverted back to SMBG during the crossover/washout period, suggesting that the effectiveness of CGM depends on uninterrupted use during treatment with MDI. Additionally, the study showed reductions in severe and nocturnal hypoglycemia as well as in glycemic variability and improved hypoglycemic confidence for rtCGM users.



Glycemic Outcomes in Adults With T1D Are Impacted More by Continuous Glucose Monitoring Than by Insulin Delivery Method: 3 Years of Follow-Up From the COMISAIR Study
June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Diabetes Care
Key Takeaway: The COMISAIR study is the longest running real-world real-time CGM (rtCGM) study performed to date. In this study, the continuous use of rtCGM had a sustained and durable benefit with regards to glycemic control over a 3-year time period, with rtCGM being superior to self-monitoring of blood glucose in reducing A1C, hypoglycemia, and glycemic variability in individuals with type 1 diabetes regardless of their insulin delivery method.
Observational COMISAIR Study in Patients With T1D Who Chose Insulin Delivery Method (MDI or Pump) and Monitoring Method (SMBG or CGM), Staying on Chosen Therapy for 3 Years

June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: The New England Journal of Medicine
Key Takeaway: This 6 month randomized trial showed use of a closed-loop system using the t:slim X2 insulin pump with Control-IQ Technology, (Tandem Diabetes Care) and a continuous glucose monitor (Dexcom G6, Dexcom) was safe and effective compared to sensor-augmented pump therapy (SAP). Participants in the closed-loop group achieved 70% time in range overall which meets the International Consensus Guidelines for people with diabetes. The closed-loop group also achieved significant improvements in hyperglycemia, HbA1c, mean glucose, and hypoglycemia (< 70 mg/dL < 54 mg/dL) as compared with the SAP group. Glycemic benefits were seen in the first month of the trial and were sustained over the entire 6-month period. Over 90% of participants said they trusted the device and found Control-IQ technology easy to use.
*Full article available for a fee
Learn More

Intermittently Scanned CGM: Novel Glucose-sensing Technology and Hypoglycaemia in Type 1 Diabetes: A Multicentre, Non-masked, Randomised Controlled Trial
June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: The Lancet
Key Takeaway: This study conducted in Europe with over 300 participants found novel flash glucose testing reduced the time adults with well controlled type 1 diabetes spent in hypoglycaemia. Future studies are needed to assess the effectiveness of this technology in patients with less well controlled diabetes and in younger age groups.
Learn More
Sign Up To Stay Current On The Latest Coverage
Updates, Recent News, And Resources


Clinical Targets for Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data Interpretation: Recommendations From the International Consensus on Time in Range
Source: Diabetes Care
Key Takeaway: Successful utilization of CGM technology in routine clinical practice remains relatively low due to a lack of clear and agreed-upon glycemic targets that both diabetes teams and people with diabetes can work toward. In February 2019, the Advanced Technologies & Treatments for Diabetes (ATTD) Congress convened an international panel of physicians, researchers, and individuals with diabetes who are expert in CGM technologies to address this issue and established targets for time in range (TIR), time below range (TBR) and time above range (TAR). These are metrics that only CGM can measure and overcome the limitations of metrics such as A1C which are reflective of a 3 month average of glycosylated hemoglobin and does not account for day to day glycemic variability or factors such as anemia which can skew A1C low.
CGM-based Targets for Different Diabetes Populations


Glycemic Outcomes with Early Initiation of Continuous Glucose Monitoring System in Recently Diagnosed Patients with Type 1 Diabetes
June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics
Key Takeaway: CGM initiated within the first year of T1D diagnosis was effective in lowering and maintaining A1C for 2.5 years and reduced the frequency of ED visits related to hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia irrespective of insulin delivery method.



Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Glycemic Control, Acute Admissions, and Quality of Life: A Real-World Study
June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Economic Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism
Key Takeaway: Nationwide reimbursement of real-time CGM improved HbA1c, fear of hypoglycemia, and QOL as well as economic indicators including work absenteeism and hospital admissions for acute diabetes complications.
The Value of rtCGM: Reduction in Hospitalizations and Work Absenteeism
Pre-Reimbursement for rtCGM Post-Reimbursement for rtCGM P Value (n = 496) (n = 379) Patients with Hospitalizations due to hypoglycemia and/or ketoacidosis 77 (16%) 14 (4%) <0.0005 Hospitalizations due to hypoglycemia 59 (11%) 12 (3%) <0.0005 Hospitalizations due to ketoacidosis 23 (5%) 4 (1%) 0.092 Work absenteesim* 123 (25%) 36 (9%) <0.0005 Days (per 100 patient years) of Hospitalizations due to hypoglycemia and/or ketoacidosis 53.5 17.8 <0.0005 Hospitalizations due to hypoglycemia 38.5 12.5 0.001 Hospitalizations due to ketoacidosis 14.9 5.3 0.220 Work absenteeism 494.5 233.8 0.001
Data are n (%).
*Work absenteeism of at least half a day. Patient-reported hospital admissions were validated by clinicians.
Reference: Charleer S, et al. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;103(3):1224–1232



Reference: Charleer S, Mathieu C, Nobels F, et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;103(3):1224-1232.
LEARN MORE

Real Time CGM Studies: Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Glycemic Control in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Using Insulin Injections – The DIAMOND Randomized Clinical Trial
June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Journal of the American Medical Association
Key Takeaway: In the DIAMOND RCT, patients using multiple daily injections of insulin with type 1 diabetes who were randomly assigned to real-time CGM (rtCGM) had improved glycemic control vs. the SMBG group. This benefit was seen across patient groups regardless of baseline A1C, age, education level, or math ability. In addition, the rtCGM group spent 79% less time in nocturnal hypoglycemia, and also demonstrated a greater increase in hypoglycemic confidence and a greater decrease in diabetes distress vs. the SMBG group.
Learn More

Baseline Glycated Hemoglobin Values Predict the Magnitude of Glycemic Improvement in Patients with Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes: Subgroup Analyses from the DIAMOND Study Program
June 16, 2020Economic Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics
Key Takeaway: Among the real-time CGM (rtCGM) users, the change in HbA1c was greatest in the highest HbA1c subgroup with similar decreases seen in both the T1D and T2D groups. Notably, adherence remained high in those with baseline HbA1c > 9% and the improvements seen were achieved without the need for additional medications. Thus, the costs of rtCGM in patients with high HbA1c may be offset by avoiding treatment intensification and the longer-term savings achieved by lowering HbA1c levels in poorly controlled diabetes populations.



Continuous Glucose Monitoring vs Conventional Therapy for Glycemic Control in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Treated with Multiple Daily Insulin Injections – The GOLD Randomized Clinical Trial
June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Journal of the American Medical Association
Key Takeaway: In the GOLD trial, glycemic control was improved with use of rtCGM compared with conventional treatment; however, increases in A1C and hypoglycemic events occurred when patients reverted back to SMBG during the crossover/washout period, suggesting that the effectiveness of CGM depends on uninterrupted use during treatment with MDI. Additionally, the study showed reductions in severe and nocturnal hypoglycemia as well as in glycemic variability and improved hypoglycemic confidence for rtCGM users.



Glycemic Outcomes in Adults With T1D Are Impacted More by Continuous Glucose Monitoring Than by Insulin Delivery Method: 3 Years of Follow-Up From the COMISAIR Study
June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Diabetes Care
Key Takeaway: The COMISAIR study is the longest running real-world real-time CGM (rtCGM) study performed to date. In this study, the continuous use of rtCGM had a sustained and durable benefit with regards to glycemic control over a 3-year time period, with rtCGM being superior to self-monitoring of blood glucose in reducing A1C, hypoglycemia, and glycemic variability in individuals with type 1 diabetes regardless of their insulin delivery method.
Observational COMISAIR Study in Patients With T1D Who Chose Insulin Delivery Method (MDI or Pump) and Monitoring Method (SMBG or CGM), Staying on Chosen Therapy for 3 Years

June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: The New England Journal of Medicine
Key Takeaway: This 6 month randomized trial showed use of a closed-loop system using the t:slim X2 insulin pump with Control-IQ Technology, (Tandem Diabetes Care) and a continuous glucose monitor (Dexcom G6, Dexcom) was safe and effective compared to sensor-augmented pump therapy (SAP). Participants in the closed-loop group achieved 70% time in range overall which meets the International Consensus Guidelines for people with diabetes. The closed-loop group also achieved significant improvements in hyperglycemia, HbA1c, mean glucose, and hypoglycemia (< 70 mg/dL < 54 mg/dL) as compared with the SAP group. Glycemic benefits were seen in the first month of the trial and were sustained over the entire 6-month period. Over 90% of participants said they trusted the device and found Control-IQ technology easy to use.
*Full article available for a fee
Learn More

Intermittently Scanned CGM: Novel Glucose-sensing Technology and Hypoglycaemia in Type 1 Diabetes: A Multicentre, Non-masked, Randomised Controlled Trial
June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: The Lancet
Key Takeaway: This study conducted in Europe with over 300 participants found novel flash glucose testing reduced the time adults with well controlled type 1 diabetes spent in hypoglycaemia. Future studies are needed to assess the effectiveness of this technology in patients with less well controlled diabetes and in younger age groups.
Learn More
Sign Up To Stay Current On The Latest Coverage
Updates, Recent News, And Resources


Glycemic Outcomes with Early Initiation of Continuous Glucose Monitoring System in Recently Diagnosed Patients with Type 1 Diabetes
Source: Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics
Key Takeaway: CGM initiated within the first year of T1D diagnosis was effective in lowering and maintaining A1C for 2.5 years and reduced the frequency of ED visits related to hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia irrespective of insulin delivery method.


Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Glycemic Control, Acute Admissions, and Quality of Life: A Real-World Study
June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Economic Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism
Key Takeaway: Nationwide reimbursement of real-time CGM improved HbA1c, fear of hypoglycemia, and QOL as well as economic indicators including work absenteeism and hospital admissions for acute diabetes complications.
The Value of rtCGM: Reduction in Hospitalizations and Work Absenteeism
Pre-Reimbursement for rtCGM Post-Reimbursement for rtCGM P Value (n = 496) (n = 379) Patients with Hospitalizations due to hypoglycemia and/or ketoacidosis 77 (16%) 14 (4%) <0.0005 Hospitalizations due to hypoglycemia 59 (11%) 12 (3%) <0.0005 Hospitalizations due to ketoacidosis 23 (5%) 4 (1%) 0.092 Work absenteesim* 123 (25%) 36 (9%) <0.0005 Days (per 100 patient years) of Hospitalizations due to hypoglycemia and/or ketoacidosis 53.5 17.8 <0.0005 Hospitalizations due to hypoglycemia 38.5 12.5 0.001 Hospitalizations due to ketoacidosis 14.9 5.3 0.220 Work absenteeism 494.5 233.8 0.001
Data are n (%).
*Work absenteeism of at least half a day. Patient-reported hospital admissions were validated by clinicians.
Reference: Charleer S, et al. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;103(3):1224–1232



Reference: Charleer S, Mathieu C, Nobels F, et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;103(3):1224-1232.
LEARN MORE

Real Time CGM Studies: Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Glycemic Control in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Using Insulin Injections – The DIAMOND Randomized Clinical Trial
June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Journal of the American Medical Association
Key Takeaway: In the DIAMOND RCT, patients using multiple daily injections of insulin with type 1 diabetes who were randomly assigned to real-time CGM (rtCGM) had improved glycemic control vs. the SMBG group. This benefit was seen across patient groups regardless of baseline A1C, age, education level, or math ability. In addition, the rtCGM group spent 79% less time in nocturnal hypoglycemia, and also demonstrated a greater increase in hypoglycemic confidence and a greater decrease in diabetes distress vs. the SMBG group.
Learn More

Baseline Glycated Hemoglobin Values Predict the Magnitude of Glycemic Improvement in Patients with Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes: Subgroup Analyses from the DIAMOND Study Program
June 16, 2020Economic Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics
Key Takeaway: Among the real-time CGM (rtCGM) users, the change in HbA1c was greatest in the highest HbA1c subgroup with similar decreases seen in both the T1D and T2D groups. Notably, adherence remained high in those with baseline HbA1c > 9% and the improvements seen were achieved without the need for additional medications. Thus, the costs of rtCGM in patients with high HbA1c may be offset by avoiding treatment intensification and the longer-term savings achieved by lowering HbA1c levels in poorly controlled diabetes populations.



Continuous Glucose Monitoring vs Conventional Therapy for Glycemic Control in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Treated with Multiple Daily Insulin Injections – The GOLD Randomized Clinical Trial
June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Journal of the American Medical Association
Key Takeaway: In the GOLD trial, glycemic control was improved with use of rtCGM compared with conventional treatment; however, increases in A1C and hypoglycemic events occurred when patients reverted back to SMBG during the crossover/washout period, suggesting that the effectiveness of CGM depends on uninterrupted use during treatment with MDI. Additionally, the study showed reductions in severe and nocturnal hypoglycemia as well as in glycemic variability and improved hypoglycemic confidence for rtCGM users.



Glycemic Outcomes in Adults With T1D Are Impacted More by Continuous Glucose Monitoring Than by Insulin Delivery Method: 3 Years of Follow-Up From the COMISAIR Study
June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Diabetes Care
Key Takeaway: The COMISAIR study is the longest running real-world real-time CGM (rtCGM) study performed to date. In this study, the continuous use of rtCGM had a sustained and durable benefit with regards to glycemic control over a 3-year time period, with rtCGM being superior to self-monitoring of blood glucose in reducing A1C, hypoglycemia, and glycemic variability in individuals with type 1 diabetes regardless of their insulin delivery method.
Observational COMISAIR Study in Patients With T1D Who Chose Insulin Delivery Method (MDI or Pump) and Monitoring Method (SMBG or CGM), Staying on Chosen Therapy for 3 Years

June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: The New England Journal of Medicine
Key Takeaway: This 6 month randomized trial showed use of a closed-loop system using the t:slim X2 insulin pump with Control-IQ Technology, (Tandem Diabetes Care) and a continuous glucose monitor (Dexcom G6, Dexcom) was safe and effective compared to sensor-augmented pump therapy (SAP). Participants in the closed-loop group achieved 70% time in range overall which meets the International Consensus Guidelines for people with diabetes. The closed-loop group also achieved significant improvements in hyperglycemia, HbA1c, mean glucose, and hypoglycemia (< 70 mg/dL < 54 mg/dL) as compared with the SAP group. Glycemic benefits were seen in the first month of the trial and were sustained over the entire 6-month period. Over 90% of participants said they trusted the device and found Control-IQ technology easy to use.
*Full article available for a fee
Learn More

Intermittently Scanned CGM: Novel Glucose-sensing Technology and Hypoglycaemia in Type 1 Diabetes: A Multicentre, Non-masked, Randomised Controlled Trial
June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: The Lancet
Key Takeaway: This study conducted in Europe with over 300 participants found novel flash glucose testing reduced the time adults with well controlled type 1 diabetes spent in hypoglycaemia. Future studies are needed to assess the effectiveness of this technology in patients with less well controlled diabetes and in younger age groups.
Learn More
Sign Up To Stay Current On The Latest Coverage
Updates, Recent News, And Resources


Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Glycemic Control, Acute Admissions, and Quality of Life: A Real-World Study
Source: The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism
Key Takeaway: Nationwide reimbursement of real-time CGM improved HbA1c, fear of hypoglycemia, and QOL as well as economic indicators including work absenteeism and hospital admissions for acute diabetes complications.
The Value of rtCGM: Reduction in Hospitalizations and Work Absenteeism
| Pre-Reimbursement for rtCGM | Post-Reimbursement for rtCGM | P Value | |
| (n = 496) | (n = 379) | ||
| Patients with | |||
| Hospitalizations due to hypoglycemia and/or ketoacidosis | 77 (16%) | 14 (4%) | <0.0005 |
| Hospitalizations due to hypoglycemia | 59 (11%) | 12 (3%) | <0.0005 |
| Hospitalizations due to ketoacidosis | 23 (5%) | 4 (1%) | 0.092 |
| Work absenteesim* | 123 (25%) | 36 (9%) | <0.0005 |
| Days (per 100 patient years) of | |||
| Hospitalizations due to hypoglycemia and/or ketoacidosis | 53.5 | 17.8 | <0.0005 |
| Hospitalizations due to hypoglycemia | 38.5 | 12.5 | 0.001 |
| Hospitalizations due to ketoacidosis | 14.9 | 5.3 | 0.220 |
| Work absenteeism | 494.5 | 233.8 | 0.001 |
Data are n (%).
*Work absenteeism of at least half a day. Patient-reported hospital admissions were validated by clinicians.
Reference: Charleer S, et al. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;103(3):1224–1232
 |  |
 |
Reference: Charleer S, Mathieu C, Nobels F, et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;103(3):1224-1232.
LEARN MORE

Real Time CGM Studies: Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Glycemic Control in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Using Insulin Injections – The DIAMOND Randomized Clinical Trial
June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Journal of the American Medical Association
Key Takeaway: In the DIAMOND RCT, patients using multiple daily injections of insulin with type 1 diabetes who were randomly assigned to real-time CGM (rtCGM) had improved glycemic control vs. the SMBG group. This benefit was seen across patient groups regardless of baseline A1C, age, education level, or math ability. In addition, the rtCGM group spent 79% less time in nocturnal hypoglycemia, and also demonstrated a greater increase in hypoglycemic confidence and a greater decrease in diabetes distress vs. the SMBG group.
Learn More

Baseline Glycated Hemoglobin Values Predict the Magnitude of Glycemic Improvement in Patients with Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes: Subgroup Analyses from the DIAMOND Study Program
June 16, 2020Economic Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics
Key Takeaway: Among the real-time CGM (rtCGM) users, the change in HbA1c was greatest in the highest HbA1c subgroup with similar decreases seen in both the T1D and T2D groups. Notably, adherence remained high in those with baseline HbA1c > 9% and the improvements seen were achieved without the need for additional medications. Thus, the costs of rtCGM in patients with high HbA1c may be offset by avoiding treatment intensification and the longer-term savings achieved by lowering HbA1c levels in poorly controlled diabetes populations.



Continuous Glucose Monitoring vs Conventional Therapy for Glycemic Control in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Treated with Multiple Daily Insulin Injections – The GOLD Randomized Clinical Trial
June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Journal of the American Medical Association
Key Takeaway: In the GOLD trial, glycemic control was improved with use of rtCGM compared with conventional treatment; however, increases in A1C and hypoglycemic events occurred when patients reverted back to SMBG during the crossover/washout period, suggesting that the effectiveness of CGM depends on uninterrupted use during treatment with MDI. Additionally, the study showed reductions in severe and nocturnal hypoglycemia as well as in glycemic variability and improved hypoglycemic confidence for rtCGM users.



Glycemic Outcomes in Adults With T1D Are Impacted More by Continuous Glucose Monitoring Than by Insulin Delivery Method: 3 Years of Follow-Up From the COMISAIR Study
June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Diabetes Care
Key Takeaway: The COMISAIR study is the longest running real-world real-time CGM (rtCGM) study performed to date. In this study, the continuous use of rtCGM had a sustained and durable benefit with regards to glycemic control over a 3-year time period, with rtCGM being superior to self-monitoring of blood glucose in reducing A1C, hypoglycemia, and glycemic variability in individuals with type 1 diabetes regardless of their insulin delivery method.
Observational COMISAIR Study in Patients With T1D Who Chose Insulin Delivery Method (MDI or Pump) and Monitoring Method (SMBG or CGM), Staying on Chosen Therapy for 3 Years

June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: The New England Journal of Medicine
Key Takeaway: This 6 month randomized trial showed use of a closed-loop system using the t:slim X2 insulin pump with Control-IQ Technology, (Tandem Diabetes Care) and a continuous glucose monitor (Dexcom G6, Dexcom) was safe and effective compared to sensor-augmented pump therapy (SAP). Participants in the closed-loop group achieved 70% time in range overall which meets the International Consensus Guidelines for people with diabetes. The closed-loop group also achieved significant improvements in hyperglycemia, HbA1c, mean glucose, and hypoglycemia (< 70 mg/dL < 54 mg/dL) as compared with the SAP group. Glycemic benefits were seen in the first month of the trial and were sustained over the entire 6-month period. Over 90% of participants said they trusted the device and found Control-IQ technology easy to use.
*Full article available for a fee
Learn More

Intermittently Scanned CGM: Novel Glucose-sensing Technology and Hypoglycaemia in Type 1 Diabetes: A Multicentre, Non-masked, Randomised Controlled Trial
June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: The Lancet
Key Takeaway: This study conducted in Europe with over 300 participants found novel flash glucose testing reduced the time adults with well controlled type 1 diabetes spent in hypoglycaemia. Future studies are needed to assess the effectiveness of this technology in patients with less well controlled diabetes and in younger age groups.
Learn More
Sign Up To Stay Current On The Latest Coverage
Updates, Recent News, And Resources


Real Time CGM Studies: Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Glycemic Control in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Using Insulin Injections – The DIAMOND Randomized Clinical Trial
Source: Journal of the American Medical Association
Key Takeaway: In the DIAMOND RCT, patients using multiple daily injections of insulin with type 1 diabetes who were randomly assigned to real-time CGM (rtCGM) had improved glycemic control vs. the SMBG group. This benefit was seen across patient groups regardless of baseline A1C, age, education level, or math ability. In addition, the rtCGM group spent 79% less time in nocturnal hypoglycemia, and also demonstrated a greater increase in hypoglycemic confidence and a greater decrease in diabetes distress vs. the SMBG group.
Learn More

Baseline Glycated Hemoglobin Values Predict the Magnitude of Glycemic Improvement in Patients with Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes: Subgroup Analyses from the DIAMOND Study Program
June 16, 2020Economic Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics
Key Takeaway: Among the real-time CGM (rtCGM) users, the change in HbA1c was greatest in the highest HbA1c subgroup with similar decreases seen in both the T1D and T2D groups. Notably, adherence remained high in those with baseline HbA1c > 9% and the improvements seen were achieved without the need for additional medications. Thus, the costs of rtCGM in patients with high HbA1c may be offset by avoiding treatment intensification and the longer-term savings achieved by lowering HbA1c levels in poorly controlled diabetes populations.



Continuous Glucose Monitoring vs Conventional Therapy for Glycemic Control in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Treated with Multiple Daily Insulin Injections – The GOLD Randomized Clinical Trial
June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Journal of the American Medical Association
Key Takeaway: In the GOLD trial, glycemic control was improved with use of rtCGM compared with conventional treatment; however, increases in A1C and hypoglycemic events occurred when patients reverted back to SMBG during the crossover/washout period, suggesting that the effectiveness of CGM depends on uninterrupted use during treatment with MDI. Additionally, the study showed reductions in severe and nocturnal hypoglycemia as well as in glycemic variability and improved hypoglycemic confidence for rtCGM users.



Glycemic Outcomes in Adults With T1D Are Impacted More by Continuous Glucose Monitoring Than by Insulin Delivery Method: 3 Years of Follow-Up From the COMISAIR Study
June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Diabetes Care
Key Takeaway: The COMISAIR study is the longest running real-world real-time CGM (rtCGM) study performed to date. In this study, the continuous use of rtCGM had a sustained and durable benefit with regards to glycemic control over a 3-year time period, with rtCGM being superior to self-monitoring of blood glucose in reducing A1C, hypoglycemia, and glycemic variability in individuals with type 1 diabetes regardless of their insulin delivery method.
Observational COMISAIR Study in Patients With T1D Who Chose Insulin Delivery Method (MDI or Pump) and Monitoring Method (SMBG or CGM), Staying on Chosen Therapy for 3 Years

June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: The New England Journal of Medicine
Key Takeaway: This 6 month randomized trial showed use of a closed-loop system using the t:slim X2 insulin pump with Control-IQ Technology, (Tandem Diabetes Care) and a continuous glucose monitor (Dexcom G6, Dexcom) was safe and effective compared to sensor-augmented pump therapy (SAP). Participants in the closed-loop group achieved 70% time in range overall which meets the International Consensus Guidelines for people with diabetes. The closed-loop group also achieved significant improvements in hyperglycemia, HbA1c, mean glucose, and hypoglycemia (< 70 mg/dL < 54 mg/dL) as compared with the SAP group. Glycemic benefits were seen in the first month of the trial and were sustained over the entire 6-month period. Over 90% of participants said they trusted the device and found Control-IQ technology easy to use.
*Full article available for a fee
Learn More

Intermittently Scanned CGM: Novel Glucose-sensing Technology and Hypoglycaemia in Type 1 Diabetes: A Multicentre, Non-masked, Randomised Controlled Trial
June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: The Lancet
Key Takeaway: This study conducted in Europe with over 300 participants found novel flash glucose testing reduced the time adults with well controlled type 1 diabetes spent in hypoglycaemia. Future studies are needed to assess the effectiveness of this technology in patients with less well controlled diabetes and in younger age groups.
Learn More
Sign Up To Stay Current On The Latest Coverage
Updates, Recent News, And Resources


Baseline Glycated Hemoglobin Values Predict the Magnitude of Glycemic Improvement in Patients with Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes: Subgroup Analyses from the DIAMOND Study Program
Source: Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics
Key Takeaway: Among the real-time CGM (rtCGM) users, the change in HbA1c was greatest in the highest HbA1c subgroup with similar decreases seen in both the T1D and T2D groups. Notably, adherence remained high in those with baseline HbA1c > 9% and the improvements seen were achieved without the need for additional medications. Thus, the costs of rtCGM in patients with high HbA1c may be offset by avoiding treatment intensification and the longer-term savings achieved by lowering HbA1c levels in poorly controlled diabetes populations.


Continuous Glucose Monitoring vs Conventional Therapy for Glycemic Control in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Treated with Multiple Daily Insulin Injections – The GOLD Randomized Clinical Trial
June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Journal of the American Medical Association
Key Takeaway: In the GOLD trial, glycemic control was improved with use of rtCGM compared with conventional treatment; however, increases in A1C and hypoglycemic events occurred when patients reverted back to SMBG during the crossover/washout period, suggesting that the effectiveness of CGM depends on uninterrupted use during treatment with MDI. Additionally, the study showed reductions in severe and nocturnal hypoglycemia as well as in glycemic variability and improved hypoglycemic confidence for rtCGM users.



Glycemic Outcomes in Adults With T1D Are Impacted More by Continuous Glucose Monitoring Than by Insulin Delivery Method: 3 Years of Follow-Up From the COMISAIR Study
June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Diabetes Care
Key Takeaway: The COMISAIR study is the longest running real-world real-time CGM (rtCGM) study performed to date. In this study, the continuous use of rtCGM had a sustained and durable benefit with regards to glycemic control over a 3-year time period, with rtCGM being superior to self-monitoring of blood glucose in reducing A1C, hypoglycemia, and glycemic variability in individuals with type 1 diabetes regardless of their insulin delivery method.
Observational COMISAIR Study in Patients With T1D Who Chose Insulin Delivery Method (MDI or Pump) and Monitoring Method (SMBG or CGM), Staying on Chosen Therapy for 3 Years

June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: The New England Journal of Medicine
Key Takeaway: This 6 month randomized trial showed use of a closed-loop system using the t:slim X2 insulin pump with Control-IQ Technology, (Tandem Diabetes Care) and a continuous glucose monitor (Dexcom G6, Dexcom) was safe and effective compared to sensor-augmented pump therapy (SAP). Participants in the closed-loop group achieved 70% time in range overall which meets the International Consensus Guidelines for people with diabetes. The closed-loop group also achieved significant improvements in hyperglycemia, HbA1c, mean glucose, and hypoglycemia (< 70 mg/dL < 54 mg/dL) as compared with the SAP group. Glycemic benefits were seen in the first month of the trial and were sustained over the entire 6-month period. Over 90% of participants said they trusted the device and found Control-IQ technology easy to use.
*Full article available for a fee
Learn More

Intermittently Scanned CGM: Novel Glucose-sensing Technology and Hypoglycaemia in Type 1 Diabetes: A Multicentre, Non-masked, Randomised Controlled Trial
June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: The Lancet
Key Takeaway: This study conducted in Europe with over 300 participants found novel flash glucose testing reduced the time adults with well controlled type 1 diabetes spent in hypoglycaemia. Future studies are needed to assess the effectiveness of this technology in patients with less well controlled diabetes and in younger age groups.
Learn More
Sign Up To Stay Current On The Latest Coverage
Updates, Recent News, And Resources


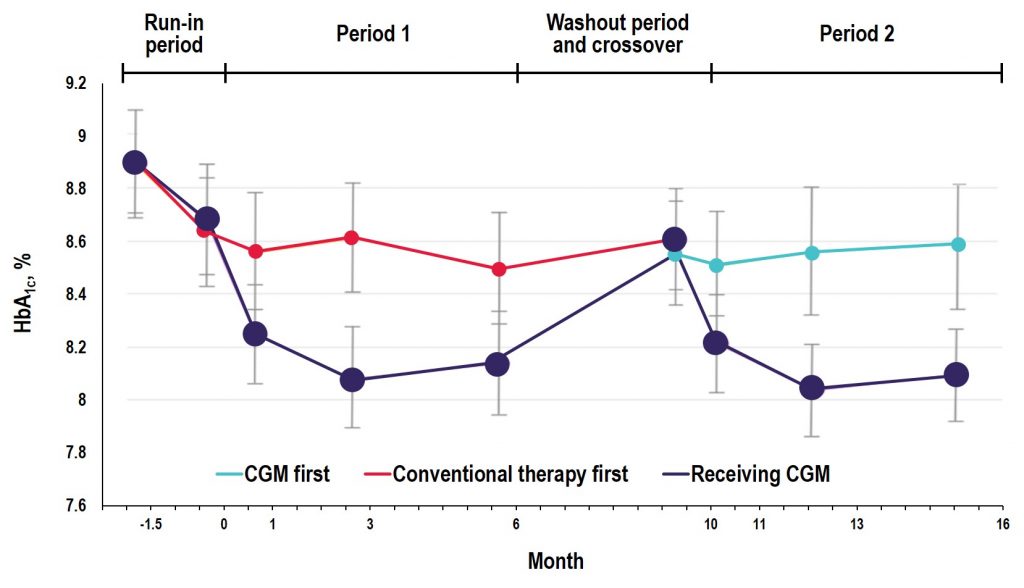
Continuous Glucose Monitoring vs Conventional Therapy for Glycemic Control in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Treated with Multiple Daily Insulin Injections – The GOLD Randomized Clinical Trial
Source: Journal of the American Medical Association
Key Takeaway: In the GOLD trial, glycemic control was improved with use of rtCGM compared with conventional treatment; however, increases in A1C and hypoglycemic events occurred when patients reverted back to SMBG during the crossover/washout period, suggesting that the effectiveness of CGM depends on uninterrupted use during treatment with MDI. Additionally, the study showed reductions in severe and nocturnal hypoglycemia as well as in glycemic variability and improved hypoglycemic confidence for rtCGM users.


Glycemic Outcomes in Adults With T1D Are Impacted More by Continuous Glucose Monitoring Than by Insulin Delivery Method: 3 Years of Follow-Up From the COMISAIR Study
June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Diabetes Care
Key Takeaway: The COMISAIR study is the longest running real-world real-time CGM (rtCGM) study performed to date. In this study, the continuous use of rtCGM had a sustained and durable benefit with regards to glycemic control over a 3-year time period, with rtCGM being superior to self-monitoring of blood glucose in reducing A1C, hypoglycemia, and glycemic variability in individuals with type 1 diabetes regardless of their insulin delivery method.
Observational COMISAIR Study in Patients With T1D Who Chose Insulin Delivery Method (MDI or Pump) and Monitoring Method (SMBG or CGM), Staying on Chosen Therapy for 3 Years

June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: The New England Journal of Medicine
Key Takeaway: This 6 month randomized trial showed use of a closed-loop system using the t:slim X2 insulin pump with Control-IQ Technology, (Tandem Diabetes Care) and a continuous glucose monitor (Dexcom G6, Dexcom) was safe and effective compared to sensor-augmented pump therapy (SAP). Participants in the closed-loop group achieved 70% time in range overall which meets the International Consensus Guidelines for people with diabetes. The closed-loop group also achieved significant improvements in hyperglycemia, HbA1c, mean glucose, and hypoglycemia (< 70 mg/dL < 54 mg/dL) as compared with the SAP group. Glycemic benefits were seen in the first month of the trial and were sustained over the entire 6-month period. Over 90% of participants said they trusted the device and found Control-IQ technology easy to use.
*Full article available for a fee
Learn More

Intermittently Scanned CGM: Novel Glucose-sensing Technology and Hypoglycaemia in Type 1 Diabetes: A Multicentre, Non-masked, Randomised Controlled Trial
June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: The Lancet
Key Takeaway: This study conducted in Europe with over 300 participants found novel flash glucose testing reduced the time adults with well controlled type 1 diabetes spent in hypoglycaemia. Future studies are needed to assess the effectiveness of this technology in patients with less well controlled diabetes and in younger age groups.
Learn More
Sign Up To Stay Current On The Latest Coverage
Updates, Recent News, And Resources


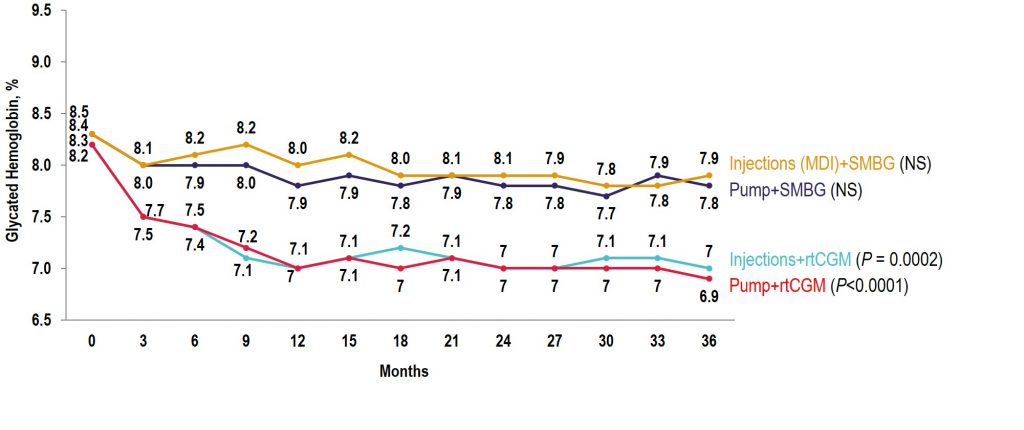
Glycemic Outcomes in Adults With T1D Are Impacted More by Continuous Glucose Monitoring Than by Insulin Delivery Method: 3 Years of Follow-Up From the COMISAIR Study
Source: Diabetes Care
Key Takeaway: The COMISAIR study is the longest running real-world real-time CGM (rtCGM) study performed to date. In this study, the continuous use of rtCGM had a sustained and durable benefit with regards to glycemic control over a 3-year time period, with rtCGM being superior to self-monitoring of blood glucose in reducing A1C, hypoglycemia, and glycemic variability in individuals with type 1 diabetes regardless of their insulin delivery method.
Observational COMISAIR Study in Patients With T1D Who Chose Insulin Delivery Method (MDI or Pump) and Monitoring Method (SMBG or CGM), Staying on Chosen Therapy for 3 Years
June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: The New England Journal of Medicine
Key Takeaway: This 6 month randomized trial showed use of a closed-loop system using the t:slim X2 insulin pump with Control-IQ Technology, (Tandem Diabetes Care) and a continuous glucose monitor (Dexcom G6, Dexcom) was safe and effective compared to sensor-augmented pump therapy (SAP). Participants in the closed-loop group achieved 70% time in range overall which meets the International Consensus Guidelines for people with diabetes. The closed-loop group also achieved significant improvements in hyperglycemia, HbA1c, mean glucose, and hypoglycemia (< 70 mg/dL < 54 mg/dL) as compared with the SAP group. Glycemic benefits were seen in the first month of the trial and were sustained over the entire 6-month period. Over 90% of participants said they trusted the device and found Control-IQ technology easy to use.
*Full article available for a fee
Learn More

Intermittently Scanned CGM: Novel Glucose-sensing Technology and Hypoglycaemia in Type 1 Diabetes: A Multicentre, Non-masked, Randomised Controlled Trial
June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: The Lancet
Key Takeaway: This study conducted in Europe with over 300 participants found novel flash glucose testing reduced the time adults with well controlled type 1 diabetes spent in hypoglycaemia. Future studies are needed to assess the effectiveness of this technology in patients with less well controlled diabetes and in younger age groups.
Learn More
Source: The New England Journal of Medicine
Key Takeaway: This 6 month randomized trial showed use of a closed-loop system using the t:slim X2 insulin pump with Control-IQ Technology, (Tandem Diabetes Care) and a continuous glucose monitor (Dexcom G6, Dexcom) was safe and effective compared to sensor-augmented pump therapy (SAP). Participants in the closed-loop group achieved 70% time in range overall which meets the International Consensus Guidelines for people with diabetes. The closed-loop group also achieved significant improvements in hyperglycemia, HbA1c, mean glucose, and hypoglycemia (< 70 mg/dL < 54 mg/dL) as compared with the SAP group. Glycemic benefits were seen in the first month of the trial and were sustained over the entire 6-month period. Over 90% of participants said they trusted the device and found Control-IQ technology easy to use.
*Full article available for a fee
Learn More

Intermittently Scanned CGM: Novel Glucose-sensing Technology and Hypoglycaemia in Type 1 Diabetes: A Multicentre, Non-masked, Randomised Controlled Trial
June 16, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: The Lancet
Key Takeaway: This study conducted in Europe with over 300 participants found novel flash glucose testing reduced the time adults with well controlled type 1 diabetes spent in hypoglycaemia. Future studies are needed to assess the effectiveness of this technology in patients with less well controlled diabetes and in younger age groups.
Learn More


Intermittently Scanned CGM: Novel Glucose-sensing Technology and Hypoglycaemia in Type 1 Diabetes: A Multicentre, Non-masked, Randomised Controlled Trial
Source: The Lancet
Key Takeaway: This study conducted in Europe with over 300 participants found novel flash glucose testing reduced the time adults with well controlled type 1 diabetes spent in hypoglycaemia. Future studies are needed to assess the effectiveness of this technology in patients with less well controlled diabetes and in younger age groups.
Learn More