Evidence


Effects of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Metrics of Glycemic Control in Diabetes: A Systematic Review With Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
October 8, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source:
Key Takeaway: A recent systematic review and meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials involving 2,461 patients showed greater improvement in mean hemoglobin A1c, time in target range, and time above range with use of real-time continuous glucose monitoring as compared to intermittently scanned continuous glucose monitoring.
Learn More

Uninterrupted Continuous Glucose Monitoring Access is Associated with a Decrease in HbA1c in Youth with Type 1 Diabetes and Public Insurance
October 8, 2020Clinical Outcomes Coverage and Benefit Design Article / Publication
Source:
Key Takeaway: In a Medicaid population of youth with Type 1 Diabetes, uninterrupted continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) use was associated with improvements in hemoglobin A1c. Interruptions in use—primarily due to gaps in insurance coverage of CGM—were associated with increased hemoglobin A1c, supporting initial and ongoing CGM coverage in high-risk, publicly insured demographics.
Learn More

Demonstrating the Clinical Impact of Continuous Glucose Monitoring Within an Integrated Healthcare Delivery System
September 24, 2020Clinical Outcomes Economic Outcomes Article / Publication
Source:
Key Takeaway: Recent data from a prospective, randomized study conducted by Intermountain Health suggests that real-time CGM can reduce healthcare utilization and decrease the overall cost of care compared to SMBG. Participants reported that real-time CGM data were helpful in modifying their nutrition, physical activity, stress, and medication adherence.
Learn MoreSeptember 1, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source:
Key Takeaway: In a 16-week trial funded by the NIDDK and Tandem Diabetes Care, 101 children ages 6-13 with type 1 diabetes were randomized to a closed-loop system of insulin delivery (n=78) or the control group (n=23) where patients used a sensor-augmented insulin pump. Children using the closed-loop system, consisting of a t:slim X2 insulin pump with Control-IQ technology and a Dexcom G6 CGM, saw a significant time in range (TIR) improvement (target 70-180 mg/dL) from 53% at baseline to 67% (equivalent to 3.4 more hours per day; p<0.001) at the end of the study. The control group saw a smaller TIR increase from 51% at baseline to 55% at the end of the study. Notably, TIR increased most significantly overnight with children reaching 80% overnight TIR compared to 54% in the control group. The treatment effect was evident in the first month and appeared consistent over 4 months. Control-IQ technology demonstrated benefits across a broad range of baseline characteristics and proved easy to use for children and their parents.
Learn More

Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Glycemic Control in Adolescents and Young Adults With Type 1 Diabetes
July 8, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Journal of the American Medical Association
Key Takeaway: Six-month, multicenter, randomized controlled trial using the Dexcom G5. The baseline population had diverse racial/ethnic backgrounds (38% Hispanic or non-white), high baseline HbA1c levels, and 41% had public health insurance. The trial showed a 0.4% A1c advantage in favor of CGM over BGM (p=0.01; baseline: 8.9%). Moreover, more than twice as many in the CGM group as compared to the BGM group achieved an A1c reduction ≥0.5% (44% vs. 21%, p=0.005) and over four-times as many participants in the CGM group vs. the BGM group saw an A1c reduction of ≥1% (25% vs. 6%, p=0.003). The CGM group also saw a 1.7 hour/day advantage vs. BGM on time-in-range (70-180 mg/dl) (p<0.001). Over two-thirds of the CGM group were using CGM at least five days/week by the end of the six-month study – the highest CGM use observed for adolescents in a study to date. Moreover, the CGM group reported significantly higher glucose monitoring satisfaction, measured via the Glucose Monitoring Satisfaction Survey score, at 26 weeks than the BGM group . Newer models of CGM devices that eliminate fingerstick calibration should lead to improved wearability and glycemic control even beyond the measured benefits observed in this trial. Improved glycemic control early in diabetes duration may prevent diabetes complications later in adulthood, making CGM an attractive option for this population.



Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Hypoglycemia in Older Adults With Type 1 Diabetes A Randomized Clinical Trial
July 8, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Journal of the American Medical Association
Key Takeaway: Older populations are more prone than younger populations to severe hypoglycemic episodes, which in turn contribute to dementia, risk of falls, glycemic variability, and mortality. To study whether CGM could reduce hypoglycemia incidence, Pratley and colleagues performed a randomized clinical trial that compared the effect of CGM (n = 103) with BGM (n = 100) in older adults (median age, 68 years) with type 1 diabetes in 22 diabetes centers across the US. The primary outcome was reduction in hypoglycemia (glucose <70mg/dL) over 6 months. Results showed that the median time in hypoglycemia was reduced from 73 minutes to 39 minutes per day in the CGM group compared with no change (from 68 minutes to 70 minutes per day) in the BGM group, an adjusted between group reduction of 27 minutes per day (95% CI, −40 to −16 min/d). Additionally, the median percentage of time with blood glucose levels below the range for severe hypoglycemia (glucose <54mg/dL) reached the goal per international guidelines (<14min/d in older adults). Moreover, only 1 severe hypoglycemic event (glucose <54mg/dL) occurred in the CGM group vs 10 in the BGM group, with 5 of those events involving seizure or loss of consciousness. 83% of participants in the CGM group used CGM at least 6 days per week during month 6 and the results did not differ by level of cognitive impairment, education level, or age. In summary, CGM reduced the time spent in the severe hypoglycemic range, which has health care use, mortality, morbidity, and economic benefits.



Leveraging Diabetes Health Technology in Managed Care and Coverage Considerations for Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring
June 16, 2020Coverage and Benefit Design Article / Publication
Announcing a new white paper based on key findings from the Therapeutic CGM Health Care Stakeholder Summit held on November 7, 2019, in Washington, DC. The stakeholder panel included payer and employer leadership along with clinical experts in the field of endocrinology. The purpose was to gather input pertinent to the coverage and application of therapeutic continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) in managed care settings. Clinical evidence supporting the clinical and economic value of rtCGM was presented and the insights of these health care stakeholders were captured en route to formulating coverage policy recommendations for the future. This input is intended to advance the uptake and appropriate coverage of evidence-based health technology interventions by managed care organizations (MCOs) and various payers.
Learn MoreJune 16, 2020CGM Technology and Digital Health Article / Publication
Source: Diabetes Care
Key Takeaways: CGM has emerged as a new standard of care for individuals with insulin-treated diabetes. Two types of CGM systems are now available: real-time CGM (rtCGM) and intermittently scanned (isCGM). rtCGM systems automatically transmit a continuous stream of glucose data to the user, provide alerts and active alarms, and transmit glucose data in real time to a smart phone and/or other display device. The current isCGM system provides the same type of data but requires the user to purposely scan the sensor to obtain information, and it does not have alerts and alarms. Both CGM technologies have significant advantages over self-monitoring of blood glucose; however, differences in the features and capabilities of the two approaches must be considered when guiding patient selection of the system that meets their individual needs.
Learn MoreJune 16, 2020CGM Technology and Digital Health Article / Publication
Source: American Journal of Managed Care
Key Takeaway: The use of CGM is proven to reduce A1C, reduce time spent in hypo- and hyperglycemia and improve time in range (TIR) for Type 1 and Type 2 patients using intensive insulin, defined as multiple daily injections of insulin or getting insulin through an insulin pump. This has resulted in guidelines and recommendations from professional societies such as the ADA recommending CGM as a standard of care for Type 1 and Type 2 patients using intensive insulin. CGM is an important monitoring tool that is best accessed by providers and patients in the pharmacy channel
Learn MoreJune 16, 2020Coverage and Benefit Design Article / Publication
Source: First Report Managed Care
Key Takeaway: Diabetes is a complex chronic disease that for some Type 1 and Type 2 patients requires the use of intensive insulin defined as 3 or more injections/day or insulin through a pump. The adverse consequences of using insulin are severe and can result in a coma, seizure or even death which leads many patients and caregivers deciding to use less insulin as prescribed preventing achievement of glycemic goals. Real-time CGM with alerts/alarms, remote monitoring and reporting can help patients use their insulin safely and effectively to achieve lower A1Cs, spend less time in hypo- and hyperglycemia and spend more time in range (TIR). The benefits of CGM are seen when it is used to make diabetes treatment decisions such as insulin dosing, diet and lifestyle in a timely manner. Accessing CGM devices via a pharmacy benefit allows patients to start CGM faster, stay safe while using insulin and engage pharmacists, providing additional support and interventions that have been shown to improve diabetes outcomes.
Learn More
Sign Up To Stay Current On The Latest Coverage
Updates, Recent News, And Resources


Effects of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Metrics of Glycemic Control in Diabetes: A Systematic Review With Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Source:
Key Takeaway: A recent systematic review and meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials involving 2,461 patients showed greater improvement in mean hemoglobin A1c, time in target range, and time above range with use of real-time continuous glucose monitoring as compared to intermittently scanned continuous glucose monitoring.
Learn More

Uninterrupted Continuous Glucose Monitoring Access is Associated with a Decrease in HbA1c in Youth with Type 1 Diabetes and Public Insurance
October 8, 2020Clinical Outcomes Coverage and Benefit Design Article / Publication
Source:
Key Takeaway: In a Medicaid population of youth with Type 1 Diabetes, uninterrupted continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) use was associated with improvements in hemoglobin A1c. Interruptions in use—primarily due to gaps in insurance coverage of CGM—were associated with increased hemoglobin A1c, supporting initial and ongoing CGM coverage in high-risk, publicly insured demographics.
Learn More

Demonstrating the Clinical Impact of Continuous Glucose Monitoring Within an Integrated Healthcare Delivery System
September 24, 2020Clinical Outcomes Economic Outcomes Article / Publication
Source:
Key Takeaway: Recent data from a prospective, randomized study conducted by Intermountain Health suggests that real-time CGM can reduce healthcare utilization and decrease the overall cost of care compared to SMBG. Participants reported that real-time CGM data were helpful in modifying their nutrition, physical activity, stress, and medication adherence.
Learn MoreSeptember 1, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source:
Key Takeaway: In a 16-week trial funded by the NIDDK and Tandem Diabetes Care, 101 children ages 6-13 with type 1 diabetes were randomized to a closed-loop system of insulin delivery (n=78) or the control group (n=23) where patients used a sensor-augmented insulin pump. Children using the closed-loop system, consisting of a t:slim X2 insulin pump with Control-IQ technology and a Dexcom G6 CGM, saw a significant time in range (TIR) improvement (target 70-180 mg/dL) from 53% at baseline to 67% (equivalent to 3.4 more hours per day; p<0.001) at the end of the study. The control group saw a smaller TIR increase from 51% at baseline to 55% at the end of the study. Notably, TIR increased most significantly overnight with children reaching 80% overnight TIR compared to 54% in the control group. The treatment effect was evident in the first month and appeared consistent over 4 months. Control-IQ technology demonstrated benefits across a broad range of baseline characteristics and proved easy to use for children and their parents.
Learn More

Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Glycemic Control in Adolescents and Young Adults With Type 1 Diabetes
July 8, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Journal of the American Medical Association
Key Takeaway: Six-month, multicenter, randomized controlled trial using the Dexcom G5. The baseline population had diverse racial/ethnic backgrounds (38% Hispanic or non-white), high baseline HbA1c levels, and 41% had public health insurance. The trial showed a 0.4% A1c advantage in favor of CGM over BGM (p=0.01; baseline: 8.9%). Moreover, more than twice as many in the CGM group as compared to the BGM group achieved an A1c reduction ≥0.5% (44% vs. 21%, p=0.005) and over four-times as many participants in the CGM group vs. the BGM group saw an A1c reduction of ≥1% (25% vs. 6%, p=0.003). The CGM group also saw a 1.7 hour/day advantage vs. BGM on time-in-range (70-180 mg/dl) (p<0.001). Over two-thirds of the CGM group were using CGM at least five days/week by the end of the six-month study – the highest CGM use observed for adolescents in a study to date. Moreover, the CGM group reported significantly higher glucose monitoring satisfaction, measured via the Glucose Monitoring Satisfaction Survey score, at 26 weeks than the BGM group . Newer models of CGM devices that eliminate fingerstick calibration should lead to improved wearability and glycemic control even beyond the measured benefits observed in this trial. Improved glycemic control early in diabetes duration may prevent diabetes complications later in adulthood, making CGM an attractive option for this population.



Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Hypoglycemia in Older Adults With Type 1 Diabetes A Randomized Clinical Trial
July 8, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Journal of the American Medical Association
Key Takeaway: Older populations are more prone than younger populations to severe hypoglycemic episodes, which in turn contribute to dementia, risk of falls, glycemic variability, and mortality. To study whether CGM could reduce hypoglycemia incidence, Pratley and colleagues performed a randomized clinical trial that compared the effect of CGM (n = 103) with BGM (n = 100) in older adults (median age, 68 years) with type 1 diabetes in 22 diabetes centers across the US. The primary outcome was reduction in hypoglycemia (glucose <70mg/dL) over 6 months. Results showed that the median time in hypoglycemia was reduced from 73 minutes to 39 minutes per day in the CGM group compared with no change (from 68 minutes to 70 minutes per day) in the BGM group, an adjusted between group reduction of 27 minutes per day (95% CI, −40 to −16 min/d). Additionally, the median percentage of time with blood glucose levels below the range for severe hypoglycemia (glucose <54mg/dL) reached the goal per international guidelines (<14min/d in older adults). Moreover, only 1 severe hypoglycemic event (glucose <54mg/dL) occurred in the CGM group vs 10 in the BGM group, with 5 of those events involving seizure or loss of consciousness. 83% of participants in the CGM group used CGM at least 6 days per week during month 6 and the results did not differ by level of cognitive impairment, education level, or age. In summary, CGM reduced the time spent in the severe hypoglycemic range, which has health care use, mortality, morbidity, and economic benefits.



Leveraging Diabetes Health Technology in Managed Care and Coverage Considerations for Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring
June 16, 2020Coverage and Benefit Design Article / Publication
Announcing a new white paper based on key findings from the Therapeutic CGM Health Care Stakeholder Summit held on November 7, 2019, in Washington, DC. The stakeholder panel included payer and employer leadership along with clinical experts in the field of endocrinology. The purpose was to gather input pertinent to the coverage and application of therapeutic continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) in managed care settings. Clinical evidence supporting the clinical and economic value of rtCGM was presented and the insights of these health care stakeholders were captured en route to formulating coverage policy recommendations for the future. This input is intended to advance the uptake and appropriate coverage of evidence-based health technology interventions by managed care organizations (MCOs) and various payers.
Learn MoreJune 16, 2020CGM Technology and Digital Health Article / Publication
Source: Diabetes Care
Key Takeaways: CGM has emerged as a new standard of care for individuals with insulin-treated diabetes. Two types of CGM systems are now available: real-time CGM (rtCGM) and intermittently scanned (isCGM). rtCGM systems automatically transmit a continuous stream of glucose data to the user, provide alerts and active alarms, and transmit glucose data in real time to a smart phone and/or other display device. The current isCGM system provides the same type of data but requires the user to purposely scan the sensor to obtain information, and it does not have alerts and alarms. Both CGM technologies have significant advantages over self-monitoring of blood glucose; however, differences in the features and capabilities of the two approaches must be considered when guiding patient selection of the system that meets their individual needs.
Learn MoreJune 16, 2020CGM Technology and Digital Health Article / Publication
Source: American Journal of Managed Care
Key Takeaway: The use of CGM is proven to reduce A1C, reduce time spent in hypo- and hyperglycemia and improve time in range (TIR) for Type 1 and Type 2 patients using intensive insulin, defined as multiple daily injections of insulin or getting insulin through an insulin pump. This has resulted in guidelines and recommendations from professional societies such as the ADA recommending CGM as a standard of care for Type 1 and Type 2 patients using intensive insulin. CGM is an important monitoring tool that is best accessed by providers and patients in the pharmacy channel
Learn MoreJune 16, 2020Coverage and Benefit Design Article / Publication
Source: First Report Managed Care
Key Takeaway: Diabetes is a complex chronic disease that for some Type 1 and Type 2 patients requires the use of intensive insulin defined as 3 or more injections/day or insulin through a pump. The adverse consequences of using insulin are severe and can result in a coma, seizure or even death which leads many patients and caregivers deciding to use less insulin as prescribed preventing achievement of glycemic goals. Real-time CGM with alerts/alarms, remote monitoring and reporting can help patients use their insulin safely and effectively to achieve lower A1Cs, spend less time in hypo- and hyperglycemia and spend more time in range (TIR). The benefits of CGM are seen when it is used to make diabetes treatment decisions such as insulin dosing, diet and lifestyle in a timely manner. Accessing CGM devices via a pharmacy benefit allows patients to start CGM faster, stay safe while using insulin and engage pharmacists, providing additional support and interventions that have been shown to improve diabetes outcomes.
Learn More
Sign Up To Stay Current On The Latest Coverage
Updates, Recent News, And Resources


Uninterrupted Continuous Glucose Monitoring Access is Associated with a Decrease in HbA1c in Youth with Type 1 Diabetes and Public Insurance
Source:
Key Takeaway: In a Medicaid population of youth with Type 1 Diabetes, uninterrupted continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) use was associated with improvements in hemoglobin A1c. Interruptions in use—primarily due to gaps in insurance coverage of CGM—were associated with increased hemoglobin A1c, supporting initial and ongoing CGM coverage in high-risk, publicly insured demographics.
Learn More

Demonstrating the Clinical Impact of Continuous Glucose Monitoring Within an Integrated Healthcare Delivery System
September 24, 2020Clinical Outcomes Economic Outcomes Article / Publication
Source:
Key Takeaway: Recent data from a prospective, randomized study conducted by Intermountain Health suggests that real-time CGM can reduce healthcare utilization and decrease the overall cost of care compared to SMBG. Participants reported that real-time CGM data were helpful in modifying their nutrition, physical activity, stress, and medication adherence.
Learn MoreSeptember 1, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source:
Key Takeaway: In a 16-week trial funded by the NIDDK and Tandem Diabetes Care, 101 children ages 6-13 with type 1 diabetes were randomized to a closed-loop system of insulin delivery (n=78) or the control group (n=23) where patients used a sensor-augmented insulin pump. Children using the closed-loop system, consisting of a t:slim X2 insulin pump with Control-IQ technology and a Dexcom G6 CGM, saw a significant time in range (TIR) improvement (target 70-180 mg/dL) from 53% at baseline to 67% (equivalent to 3.4 more hours per day; p<0.001) at the end of the study. The control group saw a smaller TIR increase from 51% at baseline to 55% at the end of the study. Notably, TIR increased most significantly overnight with children reaching 80% overnight TIR compared to 54% in the control group. The treatment effect was evident in the first month and appeared consistent over 4 months. Control-IQ technology demonstrated benefits across a broad range of baseline characteristics and proved easy to use for children and their parents.
Learn More

Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Glycemic Control in Adolescents and Young Adults With Type 1 Diabetes
July 8, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Journal of the American Medical Association
Key Takeaway: Six-month, multicenter, randomized controlled trial using the Dexcom G5. The baseline population had diverse racial/ethnic backgrounds (38% Hispanic or non-white), high baseline HbA1c levels, and 41% had public health insurance. The trial showed a 0.4% A1c advantage in favor of CGM over BGM (p=0.01; baseline: 8.9%). Moreover, more than twice as many in the CGM group as compared to the BGM group achieved an A1c reduction ≥0.5% (44% vs. 21%, p=0.005) and over four-times as many participants in the CGM group vs. the BGM group saw an A1c reduction of ≥1% (25% vs. 6%, p=0.003). The CGM group also saw a 1.7 hour/day advantage vs. BGM on time-in-range (70-180 mg/dl) (p<0.001). Over two-thirds of the CGM group were using CGM at least five days/week by the end of the six-month study – the highest CGM use observed for adolescents in a study to date. Moreover, the CGM group reported significantly higher glucose monitoring satisfaction, measured via the Glucose Monitoring Satisfaction Survey score, at 26 weeks than the BGM group . Newer models of CGM devices that eliminate fingerstick calibration should lead to improved wearability and glycemic control even beyond the measured benefits observed in this trial. Improved glycemic control early in diabetes duration may prevent diabetes complications later in adulthood, making CGM an attractive option for this population.



Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Hypoglycemia in Older Adults With Type 1 Diabetes A Randomized Clinical Trial
July 8, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Journal of the American Medical Association
Key Takeaway: Older populations are more prone than younger populations to severe hypoglycemic episodes, which in turn contribute to dementia, risk of falls, glycemic variability, and mortality. To study whether CGM could reduce hypoglycemia incidence, Pratley and colleagues performed a randomized clinical trial that compared the effect of CGM (n = 103) with BGM (n = 100) in older adults (median age, 68 years) with type 1 diabetes in 22 diabetes centers across the US. The primary outcome was reduction in hypoglycemia (glucose <70mg/dL) over 6 months. Results showed that the median time in hypoglycemia was reduced from 73 minutes to 39 minutes per day in the CGM group compared with no change (from 68 minutes to 70 minutes per day) in the BGM group, an adjusted between group reduction of 27 minutes per day (95% CI, −40 to −16 min/d). Additionally, the median percentage of time with blood glucose levels below the range for severe hypoglycemia (glucose <54mg/dL) reached the goal per international guidelines (<14min/d in older adults). Moreover, only 1 severe hypoglycemic event (glucose <54mg/dL) occurred in the CGM group vs 10 in the BGM group, with 5 of those events involving seizure or loss of consciousness. 83% of participants in the CGM group used CGM at least 6 days per week during month 6 and the results did not differ by level of cognitive impairment, education level, or age. In summary, CGM reduced the time spent in the severe hypoglycemic range, which has health care use, mortality, morbidity, and economic benefits.



Leveraging Diabetes Health Technology in Managed Care and Coverage Considerations for Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring
June 16, 2020Coverage and Benefit Design Article / Publication
Announcing a new white paper based on key findings from the Therapeutic CGM Health Care Stakeholder Summit held on November 7, 2019, in Washington, DC. The stakeholder panel included payer and employer leadership along with clinical experts in the field of endocrinology. The purpose was to gather input pertinent to the coverage and application of therapeutic continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) in managed care settings. Clinical evidence supporting the clinical and economic value of rtCGM was presented and the insights of these health care stakeholders were captured en route to formulating coverage policy recommendations for the future. This input is intended to advance the uptake and appropriate coverage of evidence-based health technology interventions by managed care organizations (MCOs) and various payers.
Learn MoreJune 16, 2020CGM Technology and Digital Health Article / Publication
Source: Diabetes Care
Key Takeaways: CGM has emerged as a new standard of care for individuals with insulin-treated diabetes. Two types of CGM systems are now available: real-time CGM (rtCGM) and intermittently scanned (isCGM). rtCGM systems automatically transmit a continuous stream of glucose data to the user, provide alerts and active alarms, and transmit glucose data in real time to a smart phone and/or other display device. The current isCGM system provides the same type of data but requires the user to purposely scan the sensor to obtain information, and it does not have alerts and alarms. Both CGM technologies have significant advantages over self-monitoring of blood glucose; however, differences in the features and capabilities of the two approaches must be considered when guiding patient selection of the system that meets their individual needs.
Learn MoreJune 16, 2020CGM Technology and Digital Health Article / Publication
Source: American Journal of Managed Care
Key Takeaway: The use of CGM is proven to reduce A1C, reduce time spent in hypo- and hyperglycemia and improve time in range (TIR) for Type 1 and Type 2 patients using intensive insulin, defined as multiple daily injections of insulin or getting insulin through an insulin pump. This has resulted in guidelines and recommendations from professional societies such as the ADA recommending CGM as a standard of care for Type 1 and Type 2 patients using intensive insulin. CGM is an important monitoring tool that is best accessed by providers and patients in the pharmacy channel
Learn MoreJune 16, 2020Coverage and Benefit Design Article / Publication
Source: First Report Managed Care
Key Takeaway: Diabetes is a complex chronic disease that for some Type 1 and Type 2 patients requires the use of intensive insulin defined as 3 or more injections/day or insulin through a pump. The adverse consequences of using insulin are severe and can result in a coma, seizure or even death which leads many patients and caregivers deciding to use less insulin as prescribed preventing achievement of glycemic goals. Real-time CGM with alerts/alarms, remote monitoring and reporting can help patients use their insulin safely and effectively to achieve lower A1Cs, spend less time in hypo- and hyperglycemia and spend more time in range (TIR). The benefits of CGM are seen when it is used to make diabetes treatment decisions such as insulin dosing, diet and lifestyle in a timely manner. Accessing CGM devices via a pharmacy benefit allows patients to start CGM faster, stay safe while using insulin and engage pharmacists, providing additional support and interventions that have been shown to improve diabetes outcomes.
Learn More
Sign Up To Stay Current On The Latest Coverage
Updates, Recent News, And Resources


Demonstrating the Clinical Impact of Continuous Glucose Monitoring Within an Integrated Healthcare Delivery System
Source:
Key Takeaway: Recent data from a prospective, randomized study conducted by Intermountain Health suggests that real-time CGM can reduce healthcare utilization and decrease the overall cost of care compared to SMBG. Participants reported that real-time CGM data were helpful in modifying their nutrition, physical activity, stress, and medication adherence.
Learn MoreSeptember 1, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source:
Key Takeaway: In a 16-week trial funded by the NIDDK and Tandem Diabetes Care, 101 children ages 6-13 with type 1 diabetes were randomized to a closed-loop system of insulin delivery (n=78) or the control group (n=23) where patients used a sensor-augmented insulin pump. Children using the closed-loop system, consisting of a t:slim X2 insulin pump with Control-IQ technology and a Dexcom G6 CGM, saw a significant time in range (TIR) improvement (target 70-180 mg/dL) from 53% at baseline to 67% (equivalent to 3.4 more hours per day; p<0.001) at the end of the study. The control group saw a smaller TIR increase from 51% at baseline to 55% at the end of the study. Notably, TIR increased most significantly overnight with children reaching 80% overnight TIR compared to 54% in the control group. The treatment effect was evident in the first month and appeared consistent over 4 months. Control-IQ technology demonstrated benefits across a broad range of baseline characteristics and proved easy to use for children and their parents.
Learn More

Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Glycemic Control in Adolescents and Young Adults With Type 1 Diabetes
July 8, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Journal of the American Medical Association
Key Takeaway: Six-month, multicenter, randomized controlled trial using the Dexcom G5. The baseline population had diverse racial/ethnic backgrounds (38% Hispanic or non-white), high baseline HbA1c levels, and 41% had public health insurance. The trial showed a 0.4% A1c advantage in favor of CGM over BGM (p=0.01; baseline: 8.9%). Moreover, more than twice as many in the CGM group as compared to the BGM group achieved an A1c reduction ≥0.5% (44% vs. 21%, p=0.005) and over four-times as many participants in the CGM group vs. the BGM group saw an A1c reduction of ≥1% (25% vs. 6%, p=0.003). The CGM group also saw a 1.7 hour/day advantage vs. BGM on time-in-range (70-180 mg/dl) (p<0.001). Over two-thirds of the CGM group were using CGM at least five days/week by the end of the six-month study – the highest CGM use observed for adolescents in a study to date. Moreover, the CGM group reported significantly higher glucose monitoring satisfaction, measured via the Glucose Monitoring Satisfaction Survey score, at 26 weeks than the BGM group . Newer models of CGM devices that eliminate fingerstick calibration should lead to improved wearability and glycemic control even beyond the measured benefits observed in this trial. Improved glycemic control early in diabetes duration may prevent diabetes complications later in adulthood, making CGM an attractive option for this population.



Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Hypoglycemia in Older Adults With Type 1 Diabetes A Randomized Clinical Trial
July 8, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Journal of the American Medical Association
Key Takeaway: Older populations are more prone than younger populations to severe hypoglycemic episodes, which in turn contribute to dementia, risk of falls, glycemic variability, and mortality. To study whether CGM could reduce hypoglycemia incidence, Pratley and colleagues performed a randomized clinical trial that compared the effect of CGM (n = 103) with BGM (n = 100) in older adults (median age, 68 years) with type 1 diabetes in 22 diabetes centers across the US. The primary outcome was reduction in hypoglycemia (glucose <70mg/dL) over 6 months. Results showed that the median time in hypoglycemia was reduced from 73 minutes to 39 minutes per day in the CGM group compared with no change (from 68 minutes to 70 minutes per day) in the BGM group, an adjusted between group reduction of 27 minutes per day (95% CI, −40 to −16 min/d). Additionally, the median percentage of time with blood glucose levels below the range for severe hypoglycemia (glucose <54mg/dL) reached the goal per international guidelines (<14min/d in older adults). Moreover, only 1 severe hypoglycemic event (glucose <54mg/dL) occurred in the CGM group vs 10 in the BGM group, with 5 of those events involving seizure or loss of consciousness. 83% of participants in the CGM group used CGM at least 6 days per week during month 6 and the results did not differ by level of cognitive impairment, education level, or age. In summary, CGM reduced the time spent in the severe hypoglycemic range, which has health care use, mortality, morbidity, and economic benefits.



Leveraging Diabetes Health Technology in Managed Care and Coverage Considerations for Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring
June 16, 2020Coverage and Benefit Design Article / Publication
Announcing a new white paper based on key findings from the Therapeutic CGM Health Care Stakeholder Summit held on November 7, 2019, in Washington, DC. The stakeholder panel included payer and employer leadership along with clinical experts in the field of endocrinology. The purpose was to gather input pertinent to the coverage and application of therapeutic continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) in managed care settings. Clinical evidence supporting the clinical and economic value of rtCGM was presented and the insights of these health care stakeholders were captured en route to formulating coverage policy recommendations for the future. This input is intended to advance the uptake and appropriate coverage of evidence-based health technology interventions by managed care organizations (MCOs) and various payers.
Learn MoreJune 16, 2020CGM Technology and Digital Health Article / Publication
Source: Diabetes Care
Key Takeaways: CGM has emerged as a new standard of care for individuals with insulin-treated diabetes. Two types of CGM systems are now available: real-time CGM (rtCGM) and intermittently scanned (isCGM). rtCGM systems automatically transmit a continuous stream of glucose data to the user, provide alerts and active alarms, and transmit glucose data in real time to a smart phone and/or other display device. The current isCGM system provides the same type of data but requires the user to purposely scan the sensor to obtain information, and it does not have alerts and alarms. Both CGM technologies have significant advantages over self-monitoring of blood glucose; however, differences in the features and capabilities of the two approaches must be considered when guiding patient selection of the system that meets their individual needs.
Learn MoreJune 16, 2020CGM Technology and Digital Health Article / Publication
Source: American Journal of Managed Care
Key Takeaway: The use of CGM is proven to reduce A1C, reduce time spent in hypo- and hyperglycemia and improve time in range (TIR) for Type 1 and Type 2 patients using intensive insulin, defined as multiple daily injections of insulin or getting insulin through an insulin pump. This has resulted in guidelines and recommendations from professional societies such as the ADA recommending CGM as a standard of care for Type 1 and Type 2 patients using intensive insulin. CGM is an important monitoring tool that is best accessed by providers and patients in the pharmacy channel
Learn MoreJune 16, 2020Coverage and Benefit Design Article / Publication
Source: First Report Managed Care
Key Takeaway: Diabetes is a complex chronic disease that for some Type 1 and Type 2 patients requires the use of intensive insulin defined as 3 or more injections/day or insulin through a pump. The adverse consequences of using insulin are severe and can result in a coma, seizure or even death which leads many patients and caregivers deciding to use less insulin as prescribed preventing achievement of glycemic goals. Real-time CGM with alerts/alarms, remote monitoring and reporting can help patients use their insulin safely and effectively to achieve lower A1Cs, spend less time in hypo- and hyperglycemia and spend more time in range (TIR). The benefits of CGM are seen when it is used to make diabetes treatment decisions such as insulin dosing, diet and lifestyle in a timely manner. Accessing CGM devices via a pharmacy benefit allows patients to start CGM faster, stay safe while using insulin and engage pharmacists, providing additional support and interventions that have been shown to improve diabetes outcomes.
Learn More
Sign Up To Stay Current On The Latest Coverage
Updates, Recent News, And Resources
Source:
Key Takeaway: In a 16-week trial funded by the NIDDK and Tandem Diabetes Care, 101 children ages 6-13 with type 1 diabetes were randomized to a closed-loop system of insulin delivery (n=78) or the control group (n=23) where patients used a sensor-augmented insulin pump. Children using the closed-loop system, consisting of a t:slim X2 insulin pump with Control-IQ technology and a Dexcom G6 CGM, saw a significant time in range (TIR) improvement (target 70-180 mg/dL) from 53% at baseline to 67% (equivalent to 3.4 more hours per day; p<0.001) at the end of the study. The control group saw a smaller TIR increase from 51% at baseline to 55% at the end of the study. Notably, TIR increased most significantly overnight with children reaching 80% overnight TIR compared to 54% in the control group. The treatment effect was evident in the first month and appeared consistent over 4 months. Control-IQ technology demonstrated benefits across a broad range of baseline characteristics and proved easy to use for children and their parents.
Learn More

Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Glycemic Control in Adolescents and Young Adults With Type 1 Diabetes
July 8, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Journal of the American Medical Association
Key Takeaway: Six-month, multicenter, randomized controlled trial using the Dexcom G5. The baseline population had diverse racial/ethnic backgrounds (38% Hispanic or non-white), high baseline HbA1c levels, and 41% had public health insurance. The trial showed a 0.4% A1c advantage in favor of CGM over BGM (p=0.01; baseline: 8.9%). Moreover, more than twice as many in the CGM group as compared to the BGM group achieved an A1c reduction ≥0.5% (44% vs. 21%, p=0.005) and over four-times as many participants in the CGM group vs. the BGM group saw an A1c reduction of ≥1% (25% vs. 6%, p=0.003). The CGM group also saw a 1.7 hour/day advantage vs. BGM on time-in-range (70-180 mg/dl) (p<0.001). Over two-thirds of the CGM group were using CGM at least five days/week by the end of the six-month study – the highest CGM use observed for adolescents in a study to date. Moreover, the CGM group reported significantly higher glucose monitoring satisfaction, measured via the Glucose Monitoring Satisfaction Survey score, at 26 weeks than the BGM group . Newer models of CGM devices that eliminate fingerstick calibration should lead to improved wearability and glycemic control even beyond the measured benefits observed in this trial. Improved glycemic control early in diabetes duration may prevent diabetes complications later in adulthood, making CGM an attractive option for this population.



Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Hypoglycemia in Older Adults With Type 1 Diabetes A Randomized Clinical Trial
July 8, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Journal of the American Medical Association
Key Takeaway: Older populations are more prone than younger populations to severe hypoglycemic episodes, which in turn contribute to dementia, risk of falls, glycemic variability, and mortality. To study whether CGM could reduce hypoglycemia incidence, Pratley and colleagues performed a randomized clinical trial that compared the effect of CGM (n = 103) with BGM (n = 100) in older adults (median age, 68 years) with type 1 diabetes in 22 diabetes centers across the US. The primary outcome was reduction in hypoglycemia (glucose <70mg/dL) over 6 months. Results showed that the median time in hypoglycemia was reduced from 73 minutes to 39 minutes per day in the CGM group compared with no change (from 68 minutes to 70 minutes per day) in the BGM group, an adjusted between group reduction of 27 minutes per day (95% CI, −40 to −16 min/d). Additionally, the median percentage of time with blood glucose levels below the range for severe hypoglycemia (glucose <54mg/dL) reached the goal per international guidelines (<14min/d in older adults). Moreover, only 1 severe hypoglycemic event (glucose <54mg/dL) occurred in the CGM group vs 10 in the BGM group, with 5 of those events involving seizure or loss of consciousness. 83% of participants in the CGM group used CGM at least 6 days per week during month 6 and the results did not differ by level of cognitive impairment, education level, or age. In summary, CGM reduced the time spent in the severe hypoglycemic range, which has health care use, mortality, morbidity, and economic benefits.



Leveraging Diabetes Health Technology in Managed Care and Coverage Considerations for Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring
June 16, 2020Coverage and Benefit Design Article / Publication
Announcing a new white paper based on key findings from the Therapeutic CGM Health Care Stakeholder Summit held on November 7, 2019, in Washington, DC. The stakeholder panel included payer and employer leadership along with clinical experts in the field of endocrinology. The purpose was to gather input pertinent to the coverage and application of therapeutic continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) in managed care settings. Clinical evidence supporting the clinical and economic value of rtCGM was presented and the insights of these health care stakeholders were captured en route to formulating coverage policy recommendations for the future. This input is intended to advance the uptake and appropriate coverage of evidence-based health technology interventions by managed care organizations (MCOs) and various payers.
Learn MoreJune 16, 2020CGM Technology and Digital Health Article / Publication
Source: Diabetes Care
Key Takeaways: CGM has emerged as a new standard of care for individuals with insulin-treated diabetes. Two types of CGM systems are now available: real-time CGM (rtCGM) and intermittently scanned (isCGM). rtCGM systems automatically transmit a continuous stream of glucose data to the user, provide alerts and active alarms, and transmit glucose data in real time to a smart phone and/or other display device. The current isCGM system provides the same type of data but requires the user to purposely scan the sensor to obtain information, and it does not have alerts and alarms. Both CGM technologies have significant advantages over self-monitoring of blood glucose; however, differences in the features and capabilities of the two approaches must be considered when guiding patient selection of the system that meets their individual needs.
Learn MoreJune 16, 2020CGM Technology and Digital Health Article / Publication
Source: American Journal of Managed Care
Key Takeaway: The use of CGM is proven to reduce A1C, reduce time spent in hypo- and hyperglycemia and improve time in range (TIR) for Type 1 and Type 2 patients using intensive insulin, defined as multiple daily injections of insulin or getting insulin through an insulin pump. This has resulted in guidelines and recommendations from professional societies such as the ADA recommending CGM as a standard of care for Type 1 and Type 2 patients using intensive insulin. CGM is an important monitoring tool that is best accessed by providers and patients in the pharmacy channel
Learn MoreJune 16, 2020Coverage and Benefit Design Article / Publication
Source: First Report Managed Care
Key Takeaway: Diabetes is a complex chronic disease that for some Type 1 and Type 2 patients requires the use of intensive insulin defined as 3 or more injections/day or insulin through a pump. The adverse consequences of using insulin are severe and can result in a coma, seizure or even death which leads many patients and caregivers deciding to use less insulin as prescribed preventing achievement of glycemic goals. Real-time CGM with alerts/alarms, remote monitoring and reporting can help patients use their insulin safely and effectively to achieve lower A1Cs, spend less time in hypo- and hyperglycemia and spend more time in range (TIR). The benefits of CGM are seen when it is used to make diabetes treatment decisions such as insulin dosing, diet and lifestyle in a timely manner. Accessing CGM devices via a pharmacy benefit allows patients to start CGM faster, stay safe while using insulin and engage pharmacists, providing additional support and interventions that have been shown to improve diabetes outcomes.
Learn More
Sign Up To Stay Current On The Latest Coverage
Updates, Recent News, And Resources


Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Glycemic Control in Adolescents and Young Adults With Type 1 Diabetes
Source: Journal of the American Medical Association
Key Takeaway: Six-month, multicenter, randomized controlled trial using the Dexcom G5. The baseline population had diverse racial/ethnic backgrounds (38% Hispanic or non-white), high baseline HbA1c levels, and 41% had public health insurance. The trial showed a 0.4% A1c advantage in favor of CGM over BGM (p=0.01; baseline: 8.9%). Moreover, more than twice as many in the CGM group as compared to the BGM group achieved an A1c reduction ≥0.5% (44% vs. 21%, p=0.005) and over four-times as many participants in the CGM group vs. the BGM group saw an A1c reduction of ≥1% (25% vs. 6%, p=0.003). The CGM group also saw a 1.7 hour/day advantage vs. BGM on time-in-range (70-180 mg/dl) (p<0.001). Over two-thirds of the CGM group were using CGM at least five days/week by the end of the six-month study – the highest CGM use observed for adolescents in a study to date. Moreover, the CGM group reported significantly higher glucose monitoring satisfaction, measured via the Glucose Monitoring Satisfaction Survey score, at 26 weeks than the BGM group . Newer models of CGM devices that eliminate fingerstick calibration should lead to improved wearability and glycemic control even beyond the measured benefits observed in this trial. Improved glycemic control early in diabetes duration may prevent diabetes complications later in adulthood, making CGM an attractive option for this population.
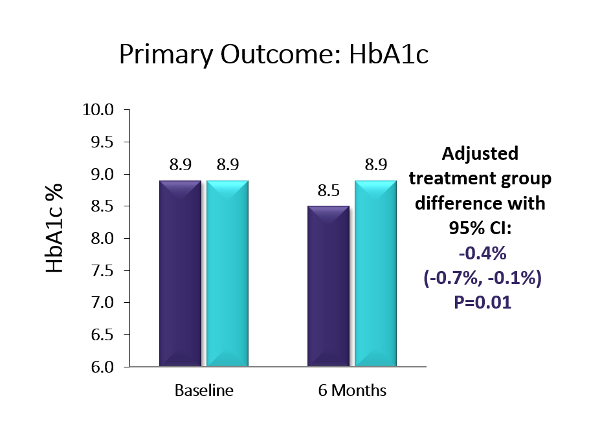


Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Hypoglycemia in Older Adults With Type 1 Diabetes A Randomized Clinical Trial
July 8, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Journal of the American Medical Association
Key Takeaway: Older populations are more prone than younger populations to severe hypoglycemic episodes, which in turn contribute to dementia, risk of falls, glycemic variability, and mortality. To study whether CGM could reduce hypoglycemia incidence, Pratley and colleagues performed a randomized clinical trial that compared the effect of CGM (n = 103) with BGM (n = 100) in older adults (median age, 68 years) with type 1 diabetes in 22 diabetes centers across the US. The primary outcome was reduction in hypoglycemia (glucose <70mg/dL) over 6 months. Results showed that the median time in hypoglycemia was reduced from 73 minutes to 39 minutes per day in the CGM group compared with no change (from 68 minutes to 70 minutes per day) in the BGM group, an adjusted between group reduction of 27 minutes per day (95% CI, −40 to −16 min/d). Additionally, the median percentage of time with blood glucose levels below the range for severe hypoglycemia (glucose <54mg/dL) reached the goal per international guidelines (<14min/d in older adults). Moreover, only 1 severe hypoglycemic event (glucose <54mg/dL) occurred in the CGM group vs 10 in the BGM group, with 5 of those events involving seizure or loss of consciousness. 83% of participants in the CGM group used CGM at least 6 days per week during month 6 and the results did not differ by level of cognitive impairment, education level, or age. In summary, CGM reduced the time spent in the severe hypoglycemic range, which has health care use, mortality, morbidity, and economic benefits.



Leveraging Diabetes Health Technology in Managed Care and Coverage Considerations for Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring
June 16, 2020Coverage and Benefit Design Article / Publication
Announcing a new white paper based on key findings from the Therapeutic CGM Health Care Stakeholder Summit held on November 7, 2019, in Washington, DC. The stakeholder panel included payer and employer leadership along with clinical experts in the field of endocrinology. The purpose was to gather input pertinent to the coverage and application of therapeutic continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) in managed care settings. Clinical evidence supporting the clinical and economic value of rtCGM was presented and the insights of these health care stakeholders were captured en route to formulating coverage policy recommendations for the future. This input is intended to advance the uptake and appropriate coverage of evidence-based health technology interventions by managed care organizations (MCOs) and various payers.
Learn MoreJune 16, 2020CGM Technology and Digital Health Article / Publication
Source: Diabetes Care
Key Takeaways: CGM has emerged as a new standard of care for individuals with insulin-treated diabetes. Two types of CGM systems are now available: real-time CGM (rtCGM) and intermittently scanned (isCGM). rtCGM systems automatically transmit a continuous stream of glucose data to the user, provide alerts and active alarms, and transmit glucose data in real time to a smart phone and/or other display device. The current isCGM system provides the same type of data but requires the user to purposely scan the sensor to obtain information, and it does not have alerts and alarms. Both CGM technologies have significant advantages over self-monitoring of blood glucose; however, differences in the features and capabilities of the two approaches must be considered when guiding patient selection of the system that meets their individual needs.
Learn MoreJune 16, 2020CGM Technology and Digital Health Article / Publication
Source: American Journal of Managed Care
Key Takeaway: The use of CGM is proven to reduce A1C, reduce time spent in hypo- and hyperglycemia and improve time in range (TIR) for Type 1 and Type 2 patients using intensive insulin, defined as multiple daily injections of insulin or getting insulin through an insulin pump. This has resulted in guidelines and recommendations from professional societies such as the ADA recommending CGM as a standard of care for Type 1 and Type 2 patients using intensive insulin. CGM is an important monitoring tool that is best accessed by providers and patients in the pharmacy channel
Learn MoreJune 16, 2020Coverage and Benefit Design Article / Publication
Source: First Report Managed Care
Key Takeaway: Diabetes is a complex chronic disease that for some Type 1 and Type 2 patients requires the use of intensive insulin defined as 3 or more injections/day or insulin through a pump. The adverse consequences of using insulin are severe and can result in a coma, seizure or even death which leads many patients and caregivers deciding to use less insulin as prescribed preventing achievement of glycemic goals. Real-time CGM with alerts/alarms, remote monitoring and reporting can help patients use their insulin safely and effectively to achieve lower A1Cs, spend less time in hypo- and hyperglycemia and spend more time in range (TIR). The benefits of CGM are seen when it is used to make diabetes treatment decisions such as insulin dosing, diet and lifestyle in a timely manner. Accessing CGM devices via a pharmacy benefit allows patients to start CGM faster, stay safe while using insulin and engage pharmacists, providing additional support and interventions that have been shown to improve diabetes outcomes.
Learn More
Sign Up To Stay Current On The Latest Coverage
Updates, Recent News, And Resources


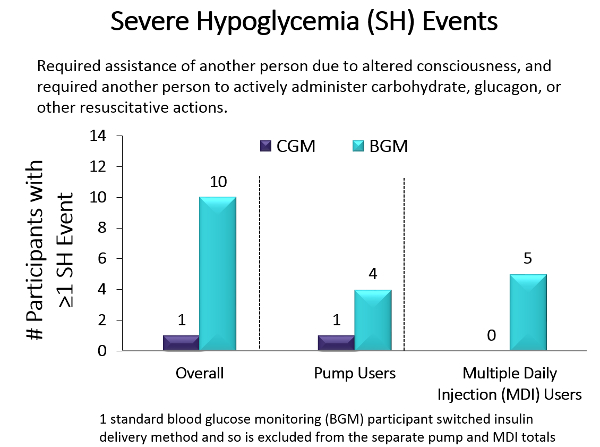
Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Hypoglycemia in Older Adults With Type 1 Diabetes A Randomized Clinical Trial
Source: Journal of the American Medical Association
Key Takeaway: Older populations are more prone than younger populations to severe hypoglycemic episodes, which in turn contribute to dementia, risk of falls, glycemic variability, and mortality. To study whether CGM could reduce hypoglycemia incidence, Pratley and colleagues performed a randomized clinical trial that compared the effect of CGM (n = 103) with BGM (n = 100) in older adults (median age, 68 years) with type 1 diabetes in 22 diabetes centers across the US. The primary outcome was reduction in hypoglycemia (glucose <70mg/dL) over 6 months. Results showed that the median time in hypoglycemia was reduced from 73 minutes to 39 minutes per day in the CGM group compared with no change (from 68 minutes to 70 minutes per day) in the BGM group, an adjusted between group reduction of 27 minutes per day (95% CI, −40 to −16 min/d). Additionally, the median percentage of time with blood glucose levels below the range for severe hypoglycemia (glucose <54mg/dL) reached the goal per international guidelines (<14min/d in older adults). Moreover, only 1 severe hypoglycemic event (glucose <54mg/dL) occurred in the CGM group vs 10 in the BGM group, with 5 of those events involving seizure or loss of consciousness. 83% of participants in the CGM group used CGM at least 6 days per week during month 6 and the results did not differ by level of cognitive impairment, education level, or age. In summary, CGM reduced the time spent in the severe hypoglycemic range, which has health care use, mortality, morbidity, and economic benefits.


Leveraging Diabetes Health Technology in Managed Care and Coverage Considerations for Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring
June 16, 2020Coverage and Benefit Design Article / Publication
Announcing a new white paper based on key findings from the Therapeutic CGM Health Care Stakeholder Summit held on November 7, 2019, in Washington, DC. The stakeholder panel included payer and employer leadership along with clinical experts in the field of endocrinology. The purpose was to gather input pertinent to the coverage and application of therapeutic continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) in managed care settings. Clinical evidence supporting the clinical and economic value of rtCGM was presented and the insights of these health care stakeholders were captured en route to formulating coverage policy recommendations for the future. This input is intended to advance the uptake and appropriate coverage of evidence-based health technology interventions by managed care organizations (MCOs) and various payers.
Learn MoreJune 16, 2020CGM Technology and Digital Health Article / Publication
Source: Diabetes Care
Key Takeaways: CGM has emerged as a new standard of care for individuals with insulin-treated diabetes. Two types of CGM systems are now available: real-time CGM (rtCGM) and intermittently scanned (isCGM). rtCGM systems automatically transmit a continuous stream of glucose data to the user, provide alerts and active alarms, and transmit glucose data in real time to a smart phone and/or other display device. The current isCGM system provides the same type of data but requires the user to purposely scan the sensor to obtain information, and it does not have alerts and alarms. Both CGM technologies have significant advantages over self-monitoring of blood glucose; however, differences in the features and capabilities of the two approaches must be considered when guiding patient selection of the system that meets their individual needs.
Learn MoreJune 16, 2020CGM Technology and Digital Health Article / Publication
Source: American Journal of Managed Care
Key Takeaway: The use of CGM is proven to reduce A1C, reduce time spent in hypo- and hyperglycemia and improve time in range (TIR) for Type 1 and Type 2 patients using intensive insulin, defined as multiple daily injections of insulin or getting insulin through an insulin pump. This has resulted in guidelines and recommendations from professional societies such as the ADA recommending CGM as a standard of care for Type 1 and Type 2 patients using intensive insulin. CGM is an important monitoring tool that is best accessed by providers and patients in the pharmacy channel
Learn MoreJune 16, 2020Coverage and Benefit Design Article / Publication
Source: First Report Managed Care
Key Takeaway: Diabetes is a complex chronic disease that for some Type 1 and Type 2 patients requires the use of intensive insulin defined as 3 or more injections/day or insulin through a pump. The adverse consequences of using insulin are severe and can result in a coma, seizure or even death which leads many patients and caregivers deciding to use less insulin as prescribed preventing achievement of glycemic goals. Real-time CGM with alerts/alarms, remote monitoring and reporting can help patients use their insulin safely and effectively to achieve lower A1Cs, spend less time in hypo- and hyperglycemia and spend more time in range (TIR). The benefits of CGM are seen when it is used to make diabetes treatment decisions such as insulin dosing, diet and lifestyle in a timely manner. Accessing CGM devices via a pharmacy benefit allows patients to start CGM faster, stay safe while using insulin and engage pharmacists, providing additional support and interventions that have been shown to improve diabetes outcomes.
Learn More
Sign Up To Stay Current On The Latest Coverage
Updates, Recent News, And Resources


Leveraging Diabetes Health Technology in Managed Care and Coverage Considerations for Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Announcing a new white paper based on key findings from the Therapeutic CGM Health Care Stakeholder Summit held on November 7, 2019, in Washington, DC. The stakeholder panel included payer and employer leadership along with clinical experts in the field of endocrinology. The purpose was to gather input pertinent to the coverage and application of therapeutic continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) in managed care settings. Clinical evidence supporting the clinical and economic value of rtCGM was presented and the insights of these health care stakeholders were captured en route to formulating coverage policy recommendations for the future. This input is intended to advance the uptake and appropriate coverage of evidence-based health technology interventions by managed care organizations (MCOs) and various payers.
Learn MoreJune 16, 2020CGM Technology and Digital Health Article / Publication
Source: Diabetes Care
Key Takeaways: CGM has emerged as a new standard of care for individuals with insulin-treated diabetes. Two types of CGM systems are now available: real-time CGM (rtCGM) and intermittently scanned (isCGM). rtCGM systems automatically transmit a continuous stream of glucose data to the user, provide alerts and active alarms, and transmit glucose data in real time to a smart phone and/or other display device. The current isCGM system provides the same type of data but requires the user to purposely scan the sensor to obtain information, and it does not have alerts and alarms. Both CGM technologies have significant advantages over self-monitoring of blood glucose; however, differences in the features and capabilities of the two approaches must be considered when guiding patient selection of the system that meets their individual needs.
Learn MoreJune 16, 2020CGM Technology and Digital Health Article / Publication
Source: American Journal of Managed Care
Key Takeaway: The use of CGM is proven to reduce A1C, reduce time spent in hypo- and hyperglycemia and improve time in range (TIR) for Type 1 and Type 2 patients using intensive insulin, defined as multiple daily injections of insulin or getting insulin through an insulin pump. This has resulted in guidelines and recommendations from professional societies such as the ADA recommending CGM as a standard of care for Type 1 and Type 2 patients using intensive insulin. CGM is an important monitoring tool that is best accessed by providers and patients in the pharmacy channel
Learn MoreJune 16, 2020Coverage and Benefit Design Article / Publication
Source: First Report Managed Care
Key Takeaway: Diabetes is a complex chronic disease that for some Type 1 and Type 2 patients requires the use of intensive insulin defined as 3 or more injections/day or insulin through a pump. The adverse consequences of using insulin are severe and can result in a coma, seizure or even death which leads many patients and caregivers deciding to use less insulin as prescribed preventing achievement of glycemic goals. Real-time CGM with alerts/alarms, remote monitoring and reporting can help patients use their insulin safely and effectively to achieve lower A1Cs, spend less time in hypo- and hyperglycemia and spend more time in range (TIR). The benefits of CGM are seen when it is used to make diabetes treatment decisions such as insulin dosing, diet and lifestyle in a timely manner. Accessing CGM devices via a pharmacy benefit allows patients to start CGM faster, stay safe while using insulin and engage pharmacists, providing additional support and interventions that have been shown to improve diabetes outcomes.
Learn More
Sign Up To Stay Current On The Latest Coverage
Updates, Recent News, And Resources
Source: Diabetes Care
Key Takeaways: CGM has emerged as a new standard of care for individuals with insulin-treated diabetes. Two types of CGM systems are now available: real-time CGM (rtCGM) and intermittently scanned (isCGM). rtCGM systems automatically transmit a continuous stream of glucose data to the user, provide alerts and active alarms, and transmit glucose data in real time to a smart phone and/or other display device. The current isCGM system provides the same type of data but requires the user to purposely scan the sensor to obtain information, and it does not have alerts and alarms. Both CGM technologies have significant advantages over self-monitoring of blood glucose; however, differences in the features and capabilities of the two approaches must be considered when guiding patient selection of the system that meets their individual needs.
Learn MoreJune 16, 2020CGM Technology and Digital Health Article / Publication
Source: American Journal of Managed Care
Key Takeaway: The use of CGM is proven to reduce A1C, reduce time spent in hypo- and hyperglycemia and improve time in range (TIR) for Type 1 and Type 2 patients using intensive insulin, defined as multiple daily injections of insulin or getting insulin through an insulin pump. This has resulted in guidelines and recommendations from professional societies such as the ADA recommending CGM as a standard of care for Type 1 and Type 2 patients using intensive insulin. CGM is an important monitoring tool that is best accessed by providers and patients in the pharmacy channel
Learn MoreJune 16, 2020Coverage and Benefit Design Article / Publication
Source: First Report Managed Care
Key Takeaway: Diabetes is a complex chronic disease that for some Type 1 and Type 2 patients requires the use of intensive insulin defined as 3 or more injections/day or insulin through a pump. The adverse consequences of using insulin are severe and can result in a coma, seizure or even death which leads many patients and caregivers deciding to use less insulin as prescribed preventing achievement of glycemic goals. Real-time CGM with alerts/alarms, remote monitoring and reporting can help patients use their insulin safely and effectively to achieve lower A1Cs, spend less time in hypo- and hyperglycemia and spend more time in range (TIR). The benefits of CGM are seen when it is used to make diabetes treatment decisions such as insulin dosing, diet and lifestyle in a timely manner. Accessing CGM devices via a pharmacy benefit allows patients to start CGM faster, stay safe while using insulin and engage pharmacists, providing additional support and interventions that have been shown to improve diabetes outcomes.
Learn More
Source: American Journal of Managed Care
Key Takeaway: The use of CGM is proven to reduce A1C, reduce time spent in hypo- and hyperglycemia and improve time in range (TIR) for Type 1 and Type 2 patients using intensive insulin, defined as multiple daily injections of insulin or getting insulin through an insulin pump. This has resulted in guidelines and recommendations from professional societies such as the ADA recommending CGM as a standard of care for Type 1 and Type 2 patients using intensive insulin. CGM is an important monitoring tool that is best accessed by providers and patients in the pharmacy channel
Learn MoreJune 16, 2020Coverage and Benefit Design Article / Publication
Source: First Report Managed Care
Key Takeaway: Diabetes is a complex chronic disease that for some Type 1 and Type 2 patients requires the use of intensive insulin defined as 3 or more injections/day or insulin through a pump. The adverse consequences of using insulin are severe and can result in a coma, seizure or even death which leads many patients and caregivers deciding to use less insulin as prescribed preventing achievement of glycemic goals. Real-time CGM with alerts/alarms, remote monitoring and reporting can help patients use their insulin safely and effectively to achieve lower A1Cs, spend less time in hypo- and hyperglycemia and spend more time in range (TIR). The benefits of CGM are seen when it is used to make diabetes treatment decisions such as insulin dosing, diet and lifestyle in a timely manner. Accessing CGM devices via a pharmacy benefit allows patients to start CGM faster, stay safe while using insulin and engage pharmacists, providing additional support and interventions that have been shown to improve diabetes outcomes.
Learn More
Source: First Report Managed Care
Key Takeaway: Diabetes is a complex chronic disease that for some Type 1 and Type 2 patients requires the use of intensive insulin defined as 3 or more injections/day or insulin through a pump. The adverse consequences of using insulin are severe and can result in a coma, seizure or even death which leads many patients and caregivers deciding to use less insulin as prescribed preventing achievement of glycemic goals. Real-time CGM with alerts/alarms, remote monitoring and reporting can help patients use their insulin safely and effectively to achieve lower A1Cs, spend less time in hypo- and hyperglycemia and spend more time in range (TIR). The benefits of CGM are seen when it is used to make diabetes treatment decisions such as insulin dosing, diet and lifestyle in a timely manner. Accessing CGM devices via a pharmacy benefit allows patients to start CGM faster, stay safe while using insulin and engage pharmacists, providing additional support and interventions that have been shown to improve diabetes outcomes.
Learn More