Evidence


Change in HbA1c and Quality of Life with Real-time CGM Use by People with Insulin-Treated Diabetes in the Landmark Study
March 1, 2021Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Diabetes Technology and Therapeutics
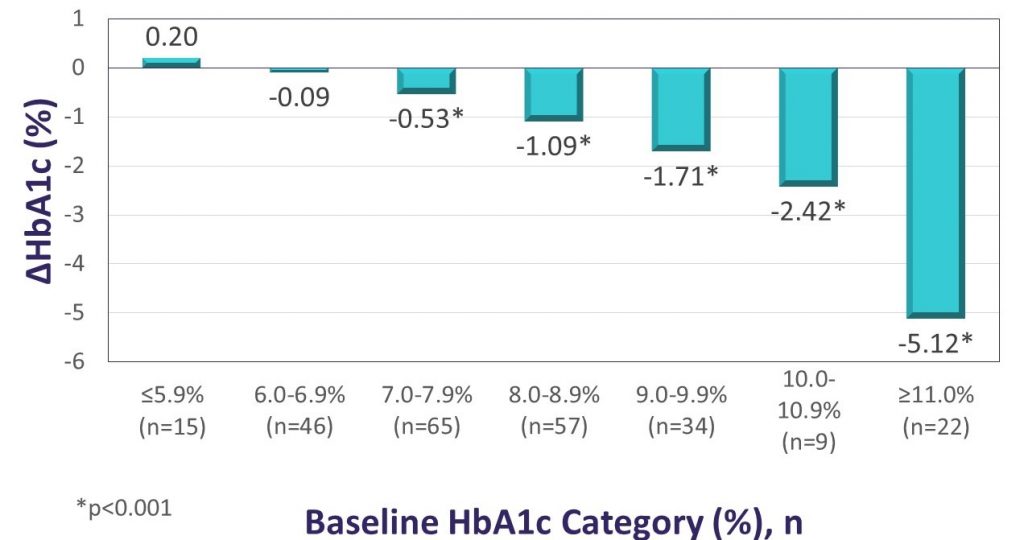
Key Takeaway: The Landmark study demonstrated significant glycemic and QoL benefits for first time CGM use among individuals using intensive insulin therapy to manage either T1D or T2D. After approximately 12 weeks of Dexcom G6 use, participants had a mean absolute reduction in HbA1c levels of 1.1%, and more than half of those with initial HbA1c values >7% experienced absolute HbA1c reductions of >1%. The reduction in HbA1c observed in Landmark was similar for patients with T1D and T2D and was more pronounced for participants with higher baseline HbA1c, consistent with observations from the DIAMOND randomized controlled trial. Significant reductions in diabetes distress and hypoglycemic concerns were also observed. In the Landmark study, there was no standardized training or intervention at CGM initiation, suggesting that the glycemic benefits can be realized without formal instruction.
Changes in HbA1c according to baseline HbA1c level
Learn MoreFebruary 26, 2021CGM Technology and Digital Health Article / Publication

Source: Association of Diabetes Care & Education Specialists and American Pharmacists Association
Key Takeaway: Developed by the Association for Diabetes Care and Education Specialists in partnership with APhA, this newly created Personal Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Implementation Playbook will help you implement a personal CGM program within your pharmacy practice.
This guide brings together fragmented information available from multiple sources to provide an inclusive and unbiased approach to implementation of Personal CGM into your practice, whatever its size. It includes a step-by-step approach to implementation, additional resources, and the latest research.
Download this free guide and start the process of incorporating this potentially game-changing tool for your patients living with diabetes.



February 26, 2021CGM Technology and Digital Health Article / PublicationSource: Association of Diabetes Care & Education Specialists and American Association of Nurse Practitioners
Key Takeaway: This toolkit provided by ADCES and AANP will help you implement a professional CGM program within your health system. Implementing a program within a healthcare setting offers many advantages, including: promotion of self-motivated, data-driven behavior change and improved clinical outcomes through alignment of medication with behavior change, resulting in lowered long-term healthcare costs for people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes.


LEARN MOREFebruary 10, 2021CGM Technology and Digital Health Article / Publication
Source: Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics
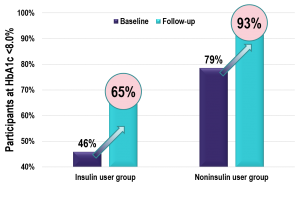
Key Takeaway: The role of real-time continuous glucose monitoring (rtCGM) is an essential component of telemedicine visits for people with diabetes. This observational study demonstrated that people with type 2 diabetes (T2D) participating in a virtual diabetes clinic can successfully insert and use Dexcom rtCGM without in-office training. The use of rtCGM was associated with a significant improvement in HbA1c at 10 months in those not meeting the ADA treatment target, independent of insulin use. In addition, there was a large shift in the percentage of participants meeting the HEDIS HbA1c target of <8.0% at follow-up; this may have important clinical and economic implications.
Chart: Percentage of Participants Achieving HEDIS HbA1c Treatment Target (HbA1c <8.0%) Before and After rtCGM Use

January 29, 2021Clinical Outcomes Guidelines / Policy
Source: National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) Guideline – Diabetes in Pregnancy: Management from Preconception to the Postnatal Period (2020)
Key Takeaway: In December 2020, NICE reviewed the evidence and changed the recommendations on intermittently scanned CGM (isCGM, also commonly referred to as flash) and continuous glucose monitoring during pregnancy for women with type 1 diabetes.
Recommendations for Managing Diabetes During Pregnancy-Intermittently scanned CGM and continuous glucose monitoring
1.3.17 Offer continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) to all pregnant women with type 1 diabetes to help them meet their pregnancy blood glucose targets and improve neonatal outcomes. 1.3.18 Offer intermittently scanned CGM (isCGM, commonly referred to as flash) to pregnant women with type 1 diabetes who are unable to use continuous glucose monitoring or express a clear preference for it. 1.3.19 Consider continuous glucose monitoring for pregnant women who are on insulin therapy but do not have type 1 diabetes, if they have problematic severe hypoglycaemia (with or without impaired awareness of hypoglycaemia) or they have unstable blood glucose levels that are causing concern despite efforts to optimise glycaemic control. 1.3.20 For pregnant women who are using isCGM or continuous glucose monitoring, a member of the joint diabetes and antenatal care team with expertise in these systems should provide education and support (including advising women about sources of out-of-hours support).
For a short explanation of why the committee made the 2020 recommendations and how they might affect practice, see the rationale and impact section on flash and continuous glucose monitoring on pages 35-36 in the Guideline. Full details of the evidence and the committee’s discussion are in evidence review A: continuous glucose monitoring.
LEARN MOREJanuary 11, 2021Coverage and Benefit Design Population Health Webinar / Archive
Presented by:
Daniel DeSalvo, MD
Assistant Professor of Pediatrics in the Section of Diabetes and Endocrinology
Baylor College of Medicine/Texas Children’s Hospital
Houston TX
In diverse and underserved populations research shows there are racial and ethnic disparities in diabetes outcomes. Disparities in diabetes technology use has the greatest influence on glycemic disparities between Black, Hispanic and Non-Hispanic White individuals. A study recently published in Diabetes Care found that lower socio-economic status was associated with lower rates of diabetes technology use and higher levels of A1C. Importantly, this gap in technology has widened over time. Data published from the T1D exchange, shows that across all age groups, individuals that use continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) have lower A1C levels compared to those who don’t use CGM.
This webinar will highlight the improvements in glycemic and psychosocial outcomes, along with best practices from recent research findings that support the use of CGM in diverse populations.
Learn MoreDecember 22, 2020Population Health CGM Best Practices / Interview
Expert: (Formerly) Vice President Clinical Strategy and Programs and Industry Relations, MagellanRx Management (Currently Chief Clinical Officer, Cooperative Benefits Group)
Summary: In this video interview Dr. Dunn discusses best practices and considerations for payers when they consider moving CGM coverage to the pharmacy benefit, application of utilization management, and more.


The Dexcom G6 Continuous Glucose Monitoring System: Outcomes and Patient Engagement from Real World Data Analytics and Clinical Practice
December 8, 2020CGM Technology and Digital Health Clinical Outcomes Economic Outcomes Webinar / Archive
Source: AMCP Science and Innovation Theater Webinar – November 17, 2020
Key Takeaway: Advances in the Dexcom G6 technology are an important CGM differentiator that allows for improved safety, glycemic management and telehealth opportunities for persons 2 years and older through the use of real-time CGM data with features such as a predictive Urgent Low Soon alert, customizable high/low glycemic threshold alerts, remote monitoring and the CLARITY diabetes management application.
Learn More

National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) Medtech Innovation Briefing for Dexcom G6 Real-Time CGM
November 3, 2020Economic Outcomes Article / Publication / CGM Innovations
Source:
Key Takeaway: The intended place in therapy is as an alternative to routine blood glucose monitoring in people (over 2 years old), including pregnant women, with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, who use multiple daily insulin injections or use insulin pumps and are self-managing their diabetes. Dexcom G6 could reduce costs and would benefit the healthcare system by improving long-term outcomes, reducing the need for intensive treatment and, in the short term, reducing severe hypoglycaemic events leading to hospital admissions. Remote care may reduce the need for hospital visits.
Learn More

Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: Real-World Data from the German/Austrian Prospective Diabetes Follow-Up Registry
October 8, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source:
Key Takeaway: Real-world data from the German/Austrian Prospective Diabetes Follow-Up Registry showed real-time continuous glucose monitoring was associated with a higher percentage of Time-in-Range and improved metabolic stability as compared to intermittent scanning continuous glucose monitoring.
Learn More
Sign Up To Stay Current On The Latest Coverage
Updates, Recent News, And Resources


Change in HbA1c and Quality of Life with Real-time CGM Use by People with Insulin-Treated Diabetes in the Landmark Study
Source: Diabetes Technology and Therapeutics
Key Takeaway: The Landmark study demonstrated significant glycemic and QoL benefits for first time CGM use among individuals using intensive insulin therapy to manage either T1D or T2D. After approximately 12 weeks of Dexcom G6 use, participants had a mean absolute reduction in HbA1c levels of 1.1%, and more than half of those with initial HbA1c values >7% experienced absolute HbA1c reductions of >1%. The reduction in HbA1c observed in Landmark was similar for patients with T1D and T2D and was more pronounced for participants with higher baseline HbA1c, consistent with observations from the DIAMOND randomized controlled trial. Significant reductions in diabetes distress and hypoglycemic concerns were also observed. In the Landmark study, there was no standardized training or intervention at CGM initiation, suggesting that the glycemic benefits can be realized without formal instruction.
Changes in HbA1c according to baseline HbA1c level
Learn MoreFebruary 26, 2021CGM Technology and Digital Health Article / Publication

Source: Association of Diabetes Care & Education Specialists and American Pharmacists Association
Key Takeaway: Developed by the Association for Diabetes Care and Education Specialists in partnership with APhA, this newly created Personal Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Implementation Playbook will help you implement a personal CGM program within your pharmacy practice.
This guide brings together fragmented information available from multiple sources to provide an inclusive and unbiased approach to implementation of Personal CGM into your practice, whatever its size. It includes a step-by-step approach to implementation, additional resources, and the latest research.
Download this free guide and start the process of incorporating this potentially game-changing tool for your patients living with diabetes.



February 26, 2021CGM Technology and Digital Health Article / PublicationSource: Association of Diabetes Care & Education Specialists and American Association of Nurse Practitioners
Key Takeaway: This toolkit provided by ADCES and AANP will help you implement a professional CGM program within your health system. Implementing a program within a healthcare setting offers many advantages, including: promotion of self-motivated, data-driven behavior change and improved clinical outcomes through alignment of medication with behavior change, resulting in lowered long-term healthcare costs for people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes.


LEARN MOREFebruary 10, 2021CGM Technology and Digital Health Article / Publication
Source: Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics
Key Takeaway: The role of real-time continuous glucose monitoring (rtCGM) is an essential component of telemedicine visits for people with diabetes. This observational study demonstrated that people with type 2 diabetes (T2D) participating in a virtual diabetes clinic can successfully insert and use Dexcom rtCGM without in-office training. The use of rtCGM was associated with a significant improvement in HbA1c at 10 months in those not meeting the ADA treatment target, independent of insulin use. In addition, there was a large shift in the percentage of participants meeting the HEDIS HbA1c target of <8.0% at follow-up; this may have important clinical and economic implications.
Chart: Percentage of Participants Achieving HEDIS HbA1c Treatment Target (HbA1c <8.0%) Before and After rtCGM Use

January 29, 2021Clinical Outcomes Guidelines / Policy
Source: National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) Guideline – Diabetes in Pregnancy: Management from Preconception to the Postnatal Period (2020)
Key Takeaway: In December 2020, NICE reviewed the evidence and changed the recommendations on intermittently scanned CGM (isCGM, also commonly referred to as flash) and continuous glucose monitoring during pregnancy for women with type 1 diabetes.
Recommendations for Managing Diabetes During Pregnancy-Intermittently scanned CGM and continuous glucose monitoring
1.3.17 Offer continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) to all pregnant women with type 1 diabetes to help them meet their pregnancy blood glucose targets and improve neonatal outcomes. 1.3.18 Offer intermittently scanned CGM (isCGM, commonly referred to as flash) to pregnant women with type 1 diabetes who are unable to use continuous glucose monitoring or express a clear preference for it. 1.3.19 Consider continuous glucose monitoring for pregnant women who are on insulin therapy but do not have type 1 diabetes, if they have problematic severe hypoglycaemia (with or without impaired awareness of hypoglycaemia) or they have unstable blood glucose levels that are causing concern despite efforts to optimise glycaemic control. 1.3.20 For pregnant women who are using isCGM or continuous glucose monitoring, a member of the joint diabetes and antenatal care team with expertise in these systems should provide education and support (including advising women about sources of out-of-hours support).
For a short explanation of why the committee made the 2020 recommendations and how they might affect practice, see the rationale and impact section on flash and continuous glucose monitoring on pages 35-36 in the Guideline. Full details of the evidence and the committee’s discussion are in evidence review A: continuous glucose monitoring.
LEARN MOREJanuary 11, 2021Coverage and Benefit Design Population Health Webinar / Archive
Presented by:
Daniel DeSalvo, MD
Assistant Professor of Pediatrics in the Section of Diabetes and Endocrinology
Baylor College of Medicine/Texas Children’s Hospital
Houston TX
In diverse and underserved populations research shows there are racial and ethnic disparities in diabetes outcomes. Disparities in diabetes technology use has the greatest influence on glycemic disparities between Black, Hispanic and Non-Hispanic White individuals. A study recently published in Diabetes Care found that lower socio-economic status was associated with lower rates of diabetes technology use and higher levels of A1C. Importantly, this gap in technology has widened over time. Data published from the T1D exchange, shows that across all age groups, individuals that use continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) have lower A1C levels compared to those who don’t use CGM.
This webinar will highlight the improvements in glycemic and psychosocial outcomes, along with best practices from recent research findings that support the use of CGM in diverse populations.
Learn MoreDecember 22, 2020Population Health CGM Best Practices / Interview
Expert: (Formerly) Vice President Clinical Strategy and Programs and Industry Relations, MagellanRx Management (Currently Chief Clinical Officer, Cooperative Benefits Group)
Summary: In this video interview Dr. Dunn discusses best practices and considerations for payers when they consider moving CGM coverage to the pharmacy benefit, application of utilization management, and more.


The Dexcom G6 Continuous Glucose Monitoring System: Outcomes and Patient Engagement from Real World Data Analytics and Clinical Practice
December 8, 2020CGM Technology and Digital Health Clinical Outcomes Economic Outcomes Webinar / Archive
Source: AMCP Science and Innovation Theater Webinar – November 17, 2020
Key Takeaway: Advances in the Dexcom G6 technology are an important CGM differentiator that allows for improved safety, glycemic management and telehealth opportunities for persons 2 years and older through the use of real-time CGM data with features such as a predictive Urgent Low Soon alert, customizable high/low glycemic threshold alerts, remote monitoring and the CLARITY diabetes management application.
Learn More

National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) Medtech Innovation Briefing for Dexcom G6 Real-Time CGM
November 3, 2020Economic Outcomes Article / Publication / CGM Innovations
Source:
Key Takeaway: The intended place in therapy is as an alternative to routine blood glucose monitoring in people (over 2 years old), including pregnant women, with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, who use multiple daily insulin injections or use insulin pumps and are self-managing their diabetes. Dexcom G6 could reduce costs and would benefit the healthcare system by improving long-term outcomes, reducing the need for intensive treatment and, in the short term, reducing severe hypoglycaemic events leading to hospital admissions. Remote care may reduce the need for hospital visits.
Learn More

Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: Real-World Data from the German/Austrian Prospective Diabetes Follow-Up Registry
October 8, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source:
Key Takeaway: Real-world data from the German/Austrian Prospective Diabetes Follow-Up Registry showed real-time continuous glucose monitoring was associated with a higher percentage of Time-in-Range and improved metabolic stability as compared to intermittent scanning continuous glucose monitoring.
Learn More
Sign Up To Stay Current On The Latest Coverage
Updates, Recent News, And Resources

Source: Association of Diabetes Care & Education Specialists and American Pharmacists Association
Key Takeaway: Developed by the Association for Diabetes Care and Education Specialists in partnership with APhA, this newly created Personal Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Implementation Playbook will help you implement a personal CGM program within your pharmacy practice.
This guide brings together fragmented information available from multiple sources to provide an inclusive and unbiased approach to implementation of Personal CGM into your practice, whatever its size. It includes a step-by-step approach to implementation, additional resources, and the latest research.
Download this free guide and start the process of incorporating this potentially game-changing tool for your patients living with diabetes.



February 26, 2021CGM Technology and Digital Health Article / PublicationSource: Association of Diabetes Care & Education Specialists and American Association of Nurse Practitioners
Key Takeaway: This toolkit provided by ADCES and AANP will help you implement a professional CGM program within your health system. Implementing a program within a healthcare setting offers many advantages, including: promotion of self-motivated, data-driven behavior change and improved clinical outcomes through alignment of medication with behavior change, resulting in lowered long-term healthcare costs for people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes.


LEARN MOREFebruary 10, 2021CGM Technology and Digital Health Article / Publication
Source: Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics
Key Takeaway: The role of real-time continuous glucose monitoring (rtCGM) is an essential component of telemedicine visits for people with diabetes. This observational study demonstrated that people with type 2 diabetes (T2D) participating in a virtual diabetes clinic can successfully insert and use Dexcom rtCGM without in-office training. The use of rtCGM was associated with a significant improvement in HbA1c at 10 months in those not meeting the ADA treatment target, independent of insulin use. In addition, there was a large shift in the percentage of participants meeting the HEDIS HbA1c target of <8.0% at follow-up; this may have important clinical and economic implications.
Chart: Percentage of Participants Achieving HEDIS HbA1c Treatment Target (HbA1c <8.0%) Before and After rtCGM Use

January 29, 2021Clinical Outcomes Guidelines / Policy
Source: National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) Guideline – Diabetes in Pregnancy: Management from Preconception to the Postnatal Period (2020)
Key Takeaway: In December 2020, NICE reviewed the evidence and changed the recommendations on intermittently scanned CGM (isCGM, also commonly referred to as flash) and continuous glucose monitoring during pregnancy for women with type 1 diabetes.
Recommendations for Managing Diabetes During Pregnancy-Intermittently scanned CGM and continuous glucose monitoring
1.3.17 Offer continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) to all pregnant women with type 1 diabetes to help them meet their pregnancy blood glucose targets and improve neonatal outcomes. 1.3.18 Offer intermittently scanned CGM (isCGM, commonly referred to as flash) to pregnant women with type 1 diabetes who are unable to use continuous glucose monitoring or express a clear preference for it. 1.3.19 Consider continuous glucose monitoring for pregnant women who are on insulin therapy but do not have type 1 diabetes, if they have problematic severe hypoglycaemia (with or without impaired awareness of hypoglycaemia) or they have unstable blood glucose levels that are causing concern despite efforts to optimise glycaemic control. 1.3.20 For pregnant women who are using isCGM or continuous glucose monitoring, a member of the joint diabetes and antenatal care team with expertise in these systems should provide education and support (including advising women about sources of out-of-hours support).
For a short explanation of why the committee made the 2020 recommendations and how they might affect practice, see the rationale and impact section on flash and continuous glucose monitoring on pages 35-36 in the Guideline. Full details of the evidence and the committee’s discussion are in evidence review A: continuous glucose monitoring.
LEARN MOREJanuary 11, 2021Coverage and Benefit Design Population Health Webinar / Archive
Presented by:
Daniel DeSalvo, MD
Assistant Professor of Pediatrics in the Section of Diabetes and Endocrinology
Baylor College of Medicine/Texas Children’s Hospital
Houston TX
In diverse and underserved populations research shows there are racial and ethnic disparities in diabetes outcomes. Disparities in diabetes technology use has the greatest influence on glycemic disparities between Black, Hispanic and Non-Hispanic White individuals. A study recently published in Diabetes Care found that lower socio-economic status was associated with lower rates of diabetes technology use and higher levels of A1C. Importantly, this gap in technology has widened over time. Data published from the T1D exchange, shows that across all age groups, individuals that use continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) have lower A1C levels compared to those who don’t use CGM.
This webinar will highlight the improvements in glycemic and psychosocial outcomes, along with best practices from recent research findings that support the use of CGM in diverse populations.
Learn MoreDecember 22, 2020Population Health CGM Best Practices / Interview
Expert: (Formerly) Vice President Clinical Strategy and Programs and Industry Relations, MagellanRx Management (Currently Chief Clinical Officer, Cooperative Benefits Group)
Summary: In this video interview Dr. Dunn discusses best practices and considerations for payers when they consider moving CGM coverage to the pharmacy benefit, application of utilization management, and more.


The Dexcom G6 Continuous Glucose Monitoring System: Outcomes and Patient Engagement from Real World Data Analytics and Clinical Practice
December 8, 2020CGM Technology and Digital Health Clinical Outcomes Economic Outcomes Webinar / Archive
Source: AMCP Science and Innovation Theater Webinar – November 17, 2020
Key Takeaway: Advances in the Dexcom G6 technology are an important CGM differentiator that allows for improved safety, glycemic management and telehealth opportunities for persons 2 years and older through the use of real-time CGM data with features such as a predictive Urgent Low Soon alert, customizable high/low glycemic threshold alerts, remote monitoring and the CLARITY diabetes management application.
Learn More

National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) Medtech Innovation Briefing for Dexcom G6 Real-Time CGM
November 3, 2020Economic Outcomes Article / Publication / CGM Innovations
Source:
Key Takeaway: The intended place in therapy is as an alternative to routine blood glucose monitoring in people (over 2 years old), including pregnant women, with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, who use multiple daily insulin injections or use insulin pumps and are self-managing their diabetes. Dexcom G6 could reduce costs and would benefit the healthcare system by improving long-term outcomes, reducing the need for intensive treatment and, in the short term, reducing severe hypoglycaemic events leading to hospital admissions. Remote care may reduce the need for hospital visits.
Learn More

Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: Real-World Data from the German/Austrian Prospective Diabetes Follow-Up Registry
October 8, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source:
Key Takeaway: Real-world data from the German/Austrian Prospective Diabetes Follow-Up Registry showed real-time continuous glucose monitoring was associated with a higher percentage of Time-in-Range and improved metabolic stability as compared to intermittent scanning continuous glucose monitoring.
Learn More
Sign Up To Stay Current On The Latest Coverage
Updates, Recent News, And Resources
Source: Association of Diabetes Care & Education Specialists and American Association of Nurse Practitioners
Key Takeaway: This toolkit provided by ADCES and AANP will help you implement a professional CGM program within your health system. Implementing a program within a healthcare setting offers many advantages, including: promotion of self-motivated, data-driven behavior change and improved clinical outcomes through alignment of medication with behavior change, resulting in lowered long-term healthcare costs for people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes.


February 10, 2021CGM Technology and Digital Health Article / Publication
Source: Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics
Key Takeaway: The role of real-time continuous glucose monitoring (rtCGM) is an essential component of telemedicine visits for people with diabetes. This observational study demonstrated that people with type 2 diabetes (T2D) participating in a virtual diabetes clinic can successfully insert and use Dexcom rtCGM without in-office training. The use of rtCGM was associated with a significant improvement in HbA1c at 10 months in those not meeting the ADA treatment target, independent of insulin use. In addition, there was a large shift in the percentage of participants meeting the HEDIS HbA1c target of <8.0% at follow-up; this may have important clinical and economic implications.
Chart: Percentage of Participants Achieving HEDIS HbA1c Treatment Target (HbA1c <8.0%) Before and After rtCGM Use

January 29, 2021Clinical Outcomes Guidelines / Policy
Source: National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) Guideline – Diabetes in Pregnancy: Management from Preconception to the Postnatal Period (2020)
Key Takeaway: In December 2020, NICE reviewed the evidence and changed the recommendations on intermittently scanned CGM (isCGM, also commonly referred to as flash) and continuous glucose monitoring during pregnancy for women with type 1 diabetes.
Recommendations for Managing Diabetes During Pregnancy-Intermittently scanned CGM and continuous glucose monitoring
1.3.17 Offer continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) to all pregnant women with type 1 diabetes to help them meet their pregnancy blood glucose targets and improve neonatal outcomes. 1.3.18 Offer intermittently scanned CGM (isCGM, commonly referred to as flash) to pregnant women with type 1 diabetes who are unable to use continuous glucose monitoring or express a clear preference for it. 1.3.19 Consider continuous glucose monitoring for pregnant women who are on insulin therapy but do not have type 1 diabetes, if they have problematic severe hypoglycaemia (with or without impaired awareness of hypoglycaemia) or they have unstable blood glucose levels that are causing concern despite efforts to optimise glycaemic control. 1.3.20 For pregnant women who are using isCGM or continuous glucose monitoring, a member of the joint diabetes and antenatal care team with expertise in these systems should provide education and support (including advising women about sources of out-of-hours support).
For a short explanation of why the committee made the 2020 recommendations and how they might affect practice, see the rationale and impact section on flash and continuous glucose monitoring on pages 35-36 in the Guideline. Full details of the evidence and the committee’s discussion are in evidence review A: continuous glucose monitoring.
LEARN MOREJanuary 11, 2021Coverage and Benefit Design Population Health Webinar / Archive
Presented by:
Daniel DeSalvo, MD
Assistant Professor of Pediatrics in the Section of Diabetes and Endocrinology
Baylor College of Medicine/Texas Children’s Hospital
Houston TX
In diverse and underserved populations research shows there are racial and ethnic disparities in diabetes outcomes. Disparities in diabetes technology use has the greatest influence on glycemic disparities between Black, Hispanic and Non-Hispanic White individuals. A study recently published in Diabetes Care found that lower socio-economic status was associated with lower rates of diabetes technology use and higher levels of A1C. Importantly, this gap in technology has widened over time. Data published from the T1D exchange, shows that across all age groups, individuals that use continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) have lower A1C levels compared to those who don’t use CGM.
This webinar will highlight the improvements in glycemic and psychosocial outcomes, along with best practices from recent research findings that support the use of CGM in diverse populations.
Learn MoreDecember 22, 2020Population Health CGM Best Practices / Interview
Expert: (Formerly) Vice President Clinical Strategy and Programs and Industry Relations, MagellanRx Management (Currently Chief Clinical Officer, Cooperative Benefits Group)
Summary: In this video interview Dr. Dunn discusses best practices and considerations for payers when they consider moving CGM coverage to the pharmacy benefit, application of utilization management, and more.


The Dexcom G6 Continuous Glucose Monitoring System: Outcomes and Patient Engagement from Real World Data Analytics and Clinical Practice
December 8, 2020CGM Technology and Digital Health Clinical Outcomes Economic Outcomes Webinar / Archive
Source: AMCP Science and Innovation Theater Webinar – November 17, 2020
Key Takeaway: Advances in the Dexcom G6 technology are an important CGM differentiator that allows for improved safety, glycemic management and telehealth opportunities for persons 2 years and older through the use of real-time CGM data with features such as a predictive Urgent Low Soon alert, customizable high/low glycemic threshold alerts, remote monitoring and the CLARITY diabetes management application.
Learn More

National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) Medtech Innovation Briefing for Dexcom G6 Real-Time CGM
November 3, 2020Economic Outcomes Article / Publication / CGM Innovations
Source:
Key Takeaway: The intended place in therapy is as an alternative to routine blood glucose monitoring in people (over 2 years old), including pregnant women, with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, who use multiple daily insulin injections or use insulin pumps and are self-managing their diabetes. Dexcom G6 could reduce costs and would benefit the healthcare system by improving long-term outcomes, reducing the need for intensive treatment and, in the short term, reducing severe hypoglycaemic events leading to hospital admissions. Remote care may reduce the need for hospital visits.
Learn More

Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: Real-World Data from the German/Austrian Prospective Diabetes Follow-Up Registry
October 8, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source:
Key Takeaway: Real-world data from the German/Austrian Prospective Diabetes Follow-Up Registry showed real-time continuous glucose monitoring was associated with a higher percentage of Time-in-Range and improved metabolic stability as compared to intermittent scanning continuous glucose monitoring.
Learn More
Sign Up To Stay Current On The Latest Coverage
Updates, Recent News, And Resources
Source: Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics
Key Takeaway: The role of real-time continuous glucose monitoring (rtCGM) is an essential component of telemedicine visits for people with diabetes. This observational study demonstrated that people with type 2 diabetes (T2D) participating in a virtual diabetes clinic can successfully insert and use Dexcom rtCGM without in-office training. The use of rtCGM was associated with a significant improvement in HbA1c at 10 months in those not meeting the ADA treatment target, independent of insulin use. In addition, there was a large shift in the percentage of participants meeting the HEDIS HbA1c target of <8.0% at follow-up; this may have important clinical and economic implications.
Chart: Percentage of Participants Achieving HEDIS HbA1c Treatment Target (HbA1c <8.0%) Before and After rtCGM Use
January 29, 2021Clinical Outcomes Guidelines / Policy
Source: National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) Guideline – Diabetes in Pregnancy: Management from Preconception to the Postnatal Period (2020)
Key Takeaway: In December 2020, NICE reviewed the evidence and changed the recommendations on intermittently scanned CGM (isCGM, also commonly referred to as flash) and continuous glucose monitoring during pregnancy for women with type 1 diabetes.
Recommendations for Managing Diabetes During Pregnancy-Intermittently scanned CGM and continuous glucose monitoring
1.3.17 Offer continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) to all pregnant women with type 1 diabetes to help them meet their pregnancy blood glucose targets and improve neonatal outcomes. 1.3.18 Offer intermittently scanned CGM (isCGM, commonly referred to as flash) to pregnant women with type 1 diabetes who are unable to use continuous glucose monitoring or express a clear preference for it. 1.3.19 Consider continuous glucose monitoring for pregnant women who are on insulin therapy but do not have type 1 diabetes, if they have problematic severe hypoglycaemia (with or without impaired awareness of hypoglycaemia) or they have unstable blood glucose levels that are causing concern despite efforts to optimise glycaemic control. 1.3.20 For pregnant women who are using isCGM or continuous glucose monitoring, a member of the joint diabetes and antenatal care team with expertise in these systems should provide education and support (including advising women about sources of out-of-hours support).
For a short explanation of why the committee made the 2020 recommendations and how they might affect practice, see the rationale and impact section on flash and continuous glucose monitoring on pages 35-36 in the Guideline. Full details of the evidence and the committee’s discussion are in evidence review A: continuous glucose monitoring.
LEARN MOREJanuary 11, 2021Coverage and Benefit Design Population Health Webinar / Archive
Presented by:
Daniel DeSalvo, MD
Assistant Professor of Pediatrics in the Section of Diabetes and Endocrinology
Baylor College of Medicine/Texas Children’s Hospital
Houston TX
In diverse and underserved populations research shows there are racial and ethnic disparities in diabetes outcomes. Disparities in diabetes technology use has the greatest influence on glycemic disparities between Black, Hispanic and Non-Hispanic White individuals. A study recently published in Diabetes Care found that lower socio-economic status was associated with lower rates of diabetes technology use and higher levels of A1C. Importantly, this gap in technology has widened over time. Data published from the T1D exchange, shows that across all age groups, individuals that use continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) have lower A1C levels compared to those who don’t use CGM.
This webinar will highlight the improvements in glycemic and psychosocial outcomes, along with best practices from recent research findings that support the use of CGM in diverse populations.
Learn MoreDecember 22, 2020Population Health CGM Best Practices / Interview
Expert: (Formerly) Vice President Clinical Strategy and Programs and Industry Relations, MagellanRx Management (Currently Chief Clinical Officer, Cooperative Benefits Group)
Summary: In this video interview Dr. Dunn discusses best practices and considerations for payers when they consider moving CGM coverage to the pharmacy benefit, application of utilization management, and more.


The Dexcom G6 Continuous Glucose Monitoring System: Outcomes and Patient Engagement from Real World Data Analytics and Clinical Practice
December 8, 2020CGM Technology and Digital Health Clinical Outcomes Economic Outcomes Webinar / Archive
Source: AMCP Science and Innovation Theater Webinar – November 17, 2020
Key Takeaway: Advances in the Dexcom G6 technology are an important CGM differentiator that allows for improved safety, glycemic management and telehealth opportunities for persons 2 years and older through the use of real-time CGM data with features such as a predictive Urgent Low Soon alert, customizable high/low glycemic threshold alerts, remote monitoring and the CLARITY diabetes management application.
Learn More

National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) Medtech Innovation Briefing for Dexcom G6 Real-Time CGM
November 3, 2020Economic Outcomes Article / Publication / CGM Innovations
Source:
Key Takeaway: The intended place in therapy is as an alternative to routine blood glucose monitoring in people (over 2 years old), including pregnant women, with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, who use multiple daily insulin injections or use insulin pumps and are self-managing their diabetes. Dexcom G6 could reduce costs and would benefit the healthcare system by improving long-term outcomes, reducing the need for intensive treatment and, in the short term, reducing severe hypoglycaemic events leading to hospital admissions. Remote care may reduce the need for hospital visits.
Learn More

Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: Real-World Data from the German/Austrian Prospective Diabetes Follow-Up Registry
October 8, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source:
Key Takeaway: Real-world data from the German/Austrian Prospective Diabetes Follow-Up Registry showed real-time continuous glucose monitoring was associated with a higher percentage of Time-in-Range and improved metabolic stability as compared to intermittent scanning continuous glucose monitoring.
Learn More
Sign Up To Stay Current On The Latest Coverage
Updates, Recent News, And Resources
Source: National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) Guideline – Diabetes in Pregnancy: Management from Preconception to the Postnatal Period (2020)
Key Takeaway: In December 2020, NICE reviewed the evidence and changed the recommendations on intermittently scanned CGM (isCGM, also commonly referred to as flash) and continuous glucose monitoring during pregnancy for women with type 1 diabetes.
Recommendations for Managing Diabetes During Pregnancy-Intermittently scanned CGM and continuous glucose monitoring
| 1.3.17 | Offer continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) to all pregnant women with type 1 diabetes to help them meet their pregnancy blood glucose targets and improve neonatal outcomes. |
| 1.3.18 | Offer intermittently scanned CGM (isCGM, commonly referred to as flash) to pregnant women with type 1 diabetes who are unable to use continuous glucose monitoring or express a clear preference for it. |
| 1.3.19 | Consider continuous glucose monitoring for pregnant women who are on insulin therapy but do not have type 1 diabetes, if they have problematic severe hypoglycaemia (with or without impaired awareness of hypoglycaemia) or they have unstable blood glucose levels that are causing concern despite efforts to optimise glycaemic control. |
| 1.3.20 | For pregnant women who are using isCGM or continuous glucose monitoring, a member of the joint diabetes and antenatal care team with expertise in these systems should provide education and support (including advising women about sources of out-of-hours support). |
For a short explanation of why the committee made the 2020 recommendations and how they might affect practice, see the rationale and impact section on flash and continuous glucose monitoring on pages 35-36 in the Guideline. Full details of the evidence and the committee’s discussion are in evidence review A: continuous glucose monitoring.
LEARN MOREJanuary 11, 2021Coverage and Benefit Design Population Health Webinar / Archive
Presented by:
Daniel DeSalvo, MD
Assistant Professor of Pediatrics in the Section of Diabetes and Endocrinology
Baylor College of Medicine/Texas Children’s Hospital
Houston TX
In diverse and underserved populations research shows there are racial and ethnic disparities in diabetes outcomes. Disparities in diabetes technology use has the greatest influence on glycemic disparities between Black, Hispanic and Non-Hispanic White individuals. A study recently published in Diabetes Care found that lower socio-economic status was associated with lower rates of diabetes technology use and higher levels of A1C. Importantly, this gap in technology has widened over time. Data published from the T1D exchange, shows that across all age groups, individuals that use continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) have lower A1C levels compared to those who don’t use CGM.
This webinar will highlight the improvements in glycemic and psychosocial outcomes, along with best practices from recent research findings that support the use of CGM in diverse populations.
Learn MoreDecember 22, 2020Population Health CGM Best Practices / Interview
Expert: (Formerly) Vice President Clinical Strategy and Programs and Industry Relations, MagellanRx Management (Currently Chief Clinical Officer, Cooperative Benefits Group)
Summary: In this video interview Dr. Dunn discusses best practices and considerations for payers when they consider moving CGM coverage to the pharmacy benefit, application of utilization management, and more.


The Dexcom G6 Continuous Glucose Monitoring System: Outcomes and Patient Engagement from Real World Data Analytics and Clinical Practice
December 8, 2020CGM Technology and Digital Health Clinical Outcomes Economic Outcomes Webinar / Archive
Source: AMCP Science and Innovation Theater Webinar – November 17, 2020
Key Takeaway: Advances in the Dexcom G6 technology are an important CGM differentiator that allows for improved safety, glycemic management and telehealth opportunities for persons 2 years and older through the use of real-time CGM data with features such as a predictive Urgent Low Soon alert, customizable high/low glycemic threshold alerts, remote monitoring and the CLARITY diabetes management application.
Learn More

National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) Medtech Innovation Briefing for Dexcom G6 Real-Time CGM
November 3, 2020Economic Outcomes Article / Publication / CGM Innovations
Source:
Key Takeaway: The intended place in therapy is as an alternative to routine blood glucose monitoring in people (over 2 years old), including pregnant women, with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, who use multiple daily insulin injections or use insulin pumps and are self-managing their diabetes. Dexcom G6 could reduce costs and would benefit the healthcare system by improving long-term outcomes, reducing the need for intensive treatment and, in the short term, reducing severe hypoglycaemic events leading to hospital admissions. Remote care may reduce the need for hospital visits.
Learn More

Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: Real-World Data from the German/Austrian Prospective Diabetes Follow-Up Registry
October 8, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source:
Key Takeaway: Real-world data from the German/Austrian Prospective Diabetes Follow-Up Registry showed real-time continuous glucose monitoring was associated with a higher percentage of Time-in-Range and improved metabolic stability as compared to intermittent scanning continuous glucose monitoring.
Learn More
Sign Up To Stay Current On The Latest Coverage
Updates, Recent News, And Resources
Presented by:
Daniel DeSalvo, MD
Assistant Professor of Pediatrics in the Section of Diabetes and Endocrinology
Baylor College of Medicine/Texas Children’s Hospital
Houston TX
In diverse and underserved populations research shows there are racial and ethnic disparities in diabetes outcomes. Disparities in diabetes technology use has the greatest influence on glycemic disparities between Black, Hispanic and Non-Hispanic White individuals. A study recently published in Diabetes Care found that lower socio-economic status was associated with lower rates of diabetes technology use and higher levels of A1C. Importantly, this gap in technology has widened over time. Data published from the T1D exchange, shows that across all age groups, individuals that use continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) have lower A1C levels compared to those who don’t use CGM.
This webinar will highlight the improvements in glycemic and psychosocial outcomes, along with best practices from recent research findings that support the use of CGM in diverse populations.
Learn MoreDecember 22, 2020Population Health CGM Best Practices / Interview
Expert: (Formerly) Vice President Clinical Strategy and Programs and Industry Relations, MagellanRx Management (Currently Chief Clinical Officer, Cooperative Benefits Group)
Summary: In this video interview Dr. Dunn discusses best practices and considerations for payers when they consider moving CGM coverage to the pharmacy benefit, application of utilization management, and more.


The Dexcom G6 Continuous Glucose Monitoring System: Outcomes and Patient Engagement from Real World Data Analytics and Clinical Practice
December 8, 2020CGM Technology and Digital Health Clinical Outcomes Economic Outcomes Webinar / Archive
Source: AMCP Science and Innovation Theater Webinar – November 17, 2020
Key Takeaway: Advances in the Dexcom G6 technology are an important CGM differentiator that allows for improved safety, glycemic management and telehealth opportunities for persons 2 years and older through the use of real-time CGM data with features such as a predictive Urgent Low Soon alert, customizable high/low glycemic threshold alerts, remote monitoring and the CLARITY diabetes management application.
Learn More

National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) Medtech Innovation Briefing for Dexcom G6 Real-Time CGM
November 3, 2020Economic Outcomes Article / Publication / CGM Innovations
Source:
Key Takeaway: The intended place in therapy is as an alternative to routine blood glucose monitoring in people (over 2 years old), including pregnant women, with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, who use multiple daily insulin injections or use insulin pumps and are self-managing their diabetes. Dexcom G6 could reduce costs and would benefit the healthcare system by improving long-term outcomes, reducing the need for intensive treatment and, in the short term, reducing severe hypoglycaemic events leading to hospital admissions. Remote care may reduce the need for hospital visits.
Learn More

Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: Real-World Data from the German/Austrian Prospective Diabetes Follow-Up Registry
October 8, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source:
Key Takeaway: Real-world data from the German/Austrian Prospective Diabetes Follow-Up Registry showed real-time continuous glucose monitoring was associated with a higher percentage of Time-in-Range and improved metabolic stability as compared to intermittent scanning continuous glucose monitoring.
Learn More
Sign Up To Stay Current On The Latest Coverage
Updates, Recent News, And Resources
Expert: (Formerly) Vice President Clinical Strategy and Programs and Industry Relations, MagellanRx Management (Currently Chief Clinical Officer, Cooperative Benefits Group)
Summary: In this video interview Dr. Dunn discusses best practices and considerations for payers when they consider moving CGM coverage to the pharmacy benefit, application of utilization management, and more.


The Dexcom G6 Continuous Glucose Monitoring System: Outcomes and Patient Engagement from Real World Data Analytics and Clinical Practice
December 8, 2020CGM Technology and Digital Health Clinical Outcomes Economic Outcomes Webinar / Archive
Source: AMCP Science and Innovation Theater Webinar – November 17, 2020
Key Takeaway: Advances in the Dexcom G6 technology are an important CGM differentiator that allows for improved safety, glycemic management and telehealth opportunities for persons 2 years and older through the use of real-time CGM data with features such as a predictive Urgent Low Soon alert, customizable high/low glycemic threshold alerts, remote monitoring and the CLARITY diabetes management application.
Learn More

National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) Medtech Innovation Briefing for Dexcom G6 Real-Time CGM
November 3, 2020Economic Outcomes Article / Publication / CGM Innovations
Source:
Key Takeaway: The intended place in therapy is as an alternative to routine blood glucose monitoring in people (over 2 years old), including pregnant women, with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, who use multiple daily insulin injections or use insulin pumps and are self-managing their diabetes. Dexcom G6 could reduce costs and would benefit the healthcare system by improving long-term outcomes, reducing the need for intensive treatment and, in the short term, reducing severe hypoglycaemic events leading to hospital admissions. Remote care may reduce the need for hospital visits.
Learn More

Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: Real-World Data from the German/Austrian Prospective Diabetes Follow-Up Registry
October 8, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source:
Key Takeaway: Real-world data from the German/Austrian Prospective Diabetes Follow-Up Registry showed real-time continuous glucose monitoring was associated with a higher percentage of Time-in-Range and improved metabolic stability as compared to intermittent scanning continuous glucose monitoring.
Learn More
Sign Up To Stay Current On The Latest Coverage
Updates, Recent News, And Resources


The Dexcom G6 Continuous Glucose Monitoring System: Outcomes and Patient Engagement from Real World Data Analytics and Clinical Practice
Source: AMCP Science and Innovation Theater Webinar – November 17, 2020
Key Takeaway: Advances in the Dexcom G6 technology are an important CGM differentiator that allows for improved safety, glycemic management and telehealth opportunities for persons 2 years and older through the use of real-time CGM data with features such as a predictive Urgent Low Soon alert, customizable high/low glycemic threshold alerts, remote monitoring and the CLARITY diabetes management application.
Learn More

National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) Medtech Innovation Briefing for Dexcom G6 Real-Time CGM
November 3, 2020Economic Outcomes Article / Publication / CGM Innovations
Source:
Key Takeaway: The intended place in therapy is as an alternative to routine blood glucose monitoring in people (over 2 years old), including pregnant women, with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, who use multiple daily insulin injections or use insulin pumps and are self-managing their diabetes. Dexcom G6 could reduce costs and would benefit the healthcare system by improving long-term outcomes, reducing the need for intensive treatment and, in the short term, reducing severe hypoglycaemic events leading to hospital admissions. Remote care may reduce the need for hospital visits.
Learn More

Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: Real-World Data from the German/Austrian Prospective Diabetes Follow-Up Registry
October 8, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source:
Key Takeaway: Real-world data from the German/Austrian Prospective Diabetes Follow-Up Registry showed real-time continuous glucose monitoring was associated with a higher percentage of Time-in-Range and improved metabolic stability as compared to intermittent scanning continuous glucose monitoring.
Learn More
Sign Up To Stay Current On The Latest Coverage
Updates, Recent News, And Resources


National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) Medtech Innovation Briefing for Dexcom G6 Real-Time CGM
Source:
Key Takeaway: The intended place in therapy is as an alternative to routine blood glucose monitoring in people (over 2 years old), including pregnant women, with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, who use multiple daily insulin injections or use insulin pumps and are self-managing their diabetes. Dexcom G6 could reduce costs and would benefit the healthcare system by improving long-term outcomes, reducing the need for intensive treatment and, in the short term, reducing severe hypoglycaemic events leading to hospital admissions. Remote care may reduce the need for hospital visits.
Learn More

Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: Real-World Data from the German/Austrian Prospective Diabetes Follow-Up Registry
October 8, 2020Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source:
Key Takeaway: Real-world data from the German/Austrian Prospective Diabetes Follow-Up Registry showed real-time continuous glucose monitoring was associated with a higher percentage of Time-in-Range and improved metabolic stability as compared to intermittent scanning continuous glucose monitoring.
Learn More


Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: Real-World Data from the German/Austrian Prospective Diabetes Follow-Up Registry
Source:
Key Takeaway: Real-world data from the German/Austrian Prospective Diabetes Follow-Up Registry showed real-time continuous glucose monitoring was associated with a higher percentage of Time-in-Range and improved metabolic stability as compared to intermittent scanning continuous glucose monitoring.
Learn More