Evidence
Search
February 3, 2022Clinical Outcomes Coverage and Benefit Design Infographic
Payer Insights Infographic



Continuous Glucose Monitoring Initiation Within First Year of Type 1 Diabetes Diagnosis Is Associated With Improved Glycemic Outcomes: 7-Year Follow-Up Study
January 12, 2022Clinical Outcomes Article / PublicationLearn MoreJanuary 4, 2022Clinical Outcomes Featured News & Info Video
October 22, 2021Coverage and Benefit Design Article / Publication / CGM Best Practices
Managed Care Insights Brief

October 11, 2021Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Endocrine Today
“Our real-world study found that in patients with insulin-treated diabetes, initiating a continuous glucose monitor substantially improved blood glucose control and cut the rate of emergency room visits for hypoglycemia in half,”
Andre J . Karter, PhD
Learn MoreSeptember 29, 2021CGM Technology and Digital Health Article / Publication

Source: Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics
Published: September 2021
Learn More

Lower A1c and Reduce Hospital/ED Use in Members with Insulin-Treated Type 2 Diabetes via Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring
September 16, 2021Clinical Outcomes Economic Outcomes Infographic



Optimize Outcomes in Insulin-Treated T1 and T2D via Evidence-Based Coverage Criteria with Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring
September 16, 2021Clinical Outcomes Coverage and Benefit Design Economic Outcomes Infographic



Association Between Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitor Use and Diabetes-Related Medical Costs for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
September 2, 2021Clinical Outcomes Economic Outcomes Article / PublicationLearn More
Sign Up To Stay Current On The Latest Coverage
Updates, Recent News, And Resources
February 3, 2022
Clinical Outcomes
Coverage and Benefit Design
Infographic
Payer Insights Infographic
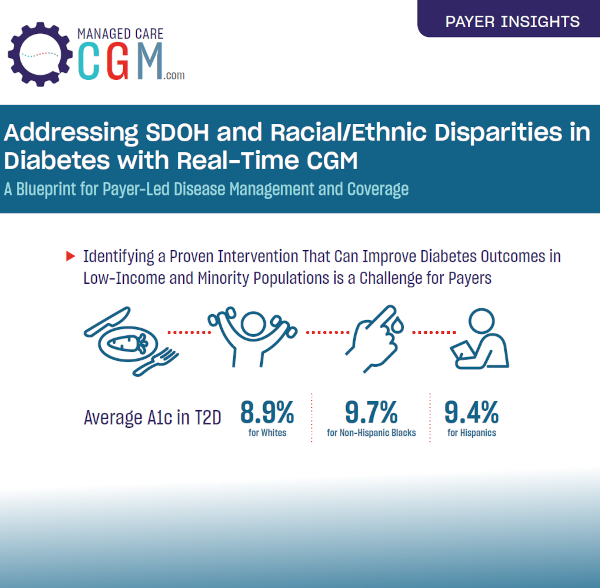


Continuous Glucose Monitoring Initiation Within First Year of Type 1 Diabetes Diagnosis Is Associated With Improved Glycemic Outcomes: 7-Year Follow-Up Study
January 12, 2022Clinical Outcomes Article / PublicationLearn MoreJanuary 4, 2022Clinical Outcomes Featured News & Info Video
October 22, 2021Coverage and Benefit Design Article / Publication / CGM Best Practices
Managed Care Insights Brief

October 11, 2021Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Endocrine Today
“Our real-world study found that in patients with insulin-treated diabetes, initiating a continuous glucose monitor substantially improved blood glucose control and cut the rate of emergency room visits for hypoglycemia in half,”
Andre J . Karter, PhD
Learn MoreSeptember 29, 2021CGM Technology and Digital Health Article / Publication

Source: Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics
Published: September 2021
Learn More

Lower A1c and Reduce Hospital/ED Use in Members with Insulin-Treated Type 2 Diabetes via Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring
September 16, 2021Clinical Outcomes Economic Outcomes Infographic



Optimize Outcomes in Insulin-Treated T1 and T2D via Evidence-Based Coverage Criteria with Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring
September 16, 2021Clinical Outcomes Coverage and Benefit Design Economic Outcomes Infographic



Association Between Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitor Use and Diabetes-Related Medical Costs for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
September 2, 2021Clinical Outcomes Economic Outcomes Article / PublicationLearn More
Sign Up To Stay Current On The Latest Coverage
Updates, Recent News, And Resources


Continuous Glucose Monitoring Initiation Within First Year of Type 1 Diabetes Diagnosis Is Associated With Improved Glycemic Outcomes: 7-Year Follow-Up Study
January 12, 2022
Clinical Outcomes
Article / Publication
January 4, 2022Clinical Outcomes Featured News & Info Video
October 22, 2021Coverage and Benefit Design Article / Publication / CGM Best Practices
Managed Care Insights Brief

October 11, 2021Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Endocrine Today
“Our real-world study found that in patients with insulin-treated diabetes, initiating a continuous glucose monitor substantially improved blood glucose control and cut the rate of emergency room visits for hypoglycemia in half,”
Andre J . Karter, PhD
Learn MoreSeptember 29, 2021CGM Technology and Digital Health Article / Publication

Source: Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics
Published: September 2021
Learn More

Lower A1c and Reduce Hospital/ED Use in Members with Insulin-Treated Type 2 Diabetes via Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring
September 16, 2021Clinical Outcomes Economic Outcomes Infographic



Optimize Outcomes in Insulin-Treated T1 and T2D via Evidence-Based Coverage Criteria with Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring
September 16, 2021Clinical Outcomes Coverage and Benefit Design Economic Outcomes Infographic



Association Between Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitor Use and Diabetes-Related Medical Costs for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
September 2, 2021Clinical Outcomes Economic Outcomes Article / PublicationLearn More
Sign Up To Stay Current On The Latest Coverage
Updates, Recent News, And Resources
January 4, 2022
Clinical Outcomes
Featured News & Info
Video
October 22, 2021Coverage and Benefit Design Article / Publication / CGM Best Practices
Managed Care Insights Brief

October 11, 2021Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Endocrine Today
“Our real-world study found that in patients with insulin-treated diabetes, initiating a continuous glucose monitor substantially improved blood glucose control and cut the rate of emergency room visits for hypoglycemia in half,”
Andre J . Karter, PhD
Learn MoreSeptember 29, 2021CGM Technology and Digital Health Article / Publication

Source: Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics
Published: September 2021
Learn More

Lower A1c and Reduce Hospital/ED Use in Members with Insulin-Treated Type 2 Diabetes via Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring
September 16, 2021Clinical Outcomes Economic Outcomes Infographic



Optimize Outcomes in Insulin-Treated T1 and T2D via Evidence-Based Coverage Criteria with Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring
September 16, 2021Clinical Outcomes Coverage and Benefit Design Economic Outcomes Infographic



Association Between Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitor Use and Diabetes-Related Medical Costs for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
September 2, 2021Clinical Outcomes Economic Outcomes Article / PublicationLearn More
Sign Up To Stay Current On The Latest Coverage
Updates, Recent News, And Resources
October 22, 2021
Coverage and Benefit Design
Article / Publication / CGM Best Practices
Managed Care Insights Brief

October 11, 2021Clinical Outcomes Article / Publication
Source: Endocrine Today
“Our real-world study found that in patients with insulin-treated diabetes, initiating a continuous glucose monitor substantially improved blood glucose control and cut the rate of emergency room visits for hypoglycemia in half,”
Andre J . Karter, PhD
Learn MoreSeptember 29, 2021CGM Technology and Digital Health Article / Publication

Source: Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics
Published: September 2021
Learn More

Lower A1c and Reduce Hospital/ED Use in Members with Insulin-Treated Type 2 Diabetes via Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring
September 16, 2021Clinical Outcomes Economic Outcomes Infographic



Optimize Outcomes in Insulin-Treated T1 and T2D via Evidence-Based Coverage Criteria with Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring
September 16, 2021Clinical Outcomes Coverage and Benefit Design Economic Outcomes Infographic



Association Between Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitor Use and Diabetes-Related Medical Costs for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
September 2, 2021Clinical Outcomes Economic Outcomes Article / PublicationLearn More
Sign Up To Stay Current On The Latest Coverage
Updates, Recent News, And Resources
October 11, 2021
Clinical Outcomes
Article / Publication
Source: Endocrine Today
“Our real-world study found that in patients with insulin-treated diabetes, initiating a continuous glucose monitor substantially improved blood glucose control and cut the rate of emergency room visits for hypoglycemia in half,”
Andre J . Karter, PhD
Learn More
September 29, 2021CGM Technology and Digital Health Article / Publication

Source: Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics
Published: September 2021
Learn More

Lower A1c and Reduce Hospital/ED Use in Members with Insulin-Treated Type 2 Diabetes via Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring
September 16, 2021Clinical Outcomes Economic Outcomes Infographic



Optimize Outcomes in Insulin-Treated T1 and T2D via Evidence-Based Coverage Criteria with Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring
September 16, 2021Clinical Outcomes Coverage and Benefit Design Economic Outcomes Infographic



Association Between Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitor Use and Diabetes-Related Medical Costs for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
September 2, 2021Clinical Outcomes Economic Outcomes Article / PublicationLearn More
Sign Up To Stay Current On The Latest Coverage
Updates, Recent News, And Resources
September 29, 2021
CGM Technology and Digital Health
Article / Publication

Source: Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics
Published: September 2021
Learn More

Lower A1c and Reduce Hospital/ED Use in Members with Insulin-Treated Type 2 Diabetes via Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring
September 16, 2021Clinical Outcomes Economic Outcomes Infographic



Optimize Outcomes in Insulin-Treated T1 and T2D via Evidence-Based Coverage Criteria with Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring
September 16, 2021Clinical Outcomes Coverage and Benefit Design Economic Outcomes Infographic



Association Between Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitor Use and Diabetes-Related Medical Costs for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
September 2, 2021Clinical Outcomes Economic Outcomes Article / PublicationLearn More
Sign Up To Stay Current On The Latest Coverage
Updates, Recent News, And Resources


Lower A1c and Reduce Hospital/ED Use in Members with Insulin-Treated Type 2 Diabetes via Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring
September 16, 2021
Clinical Outcomes
Economic Outcomes
Infographic
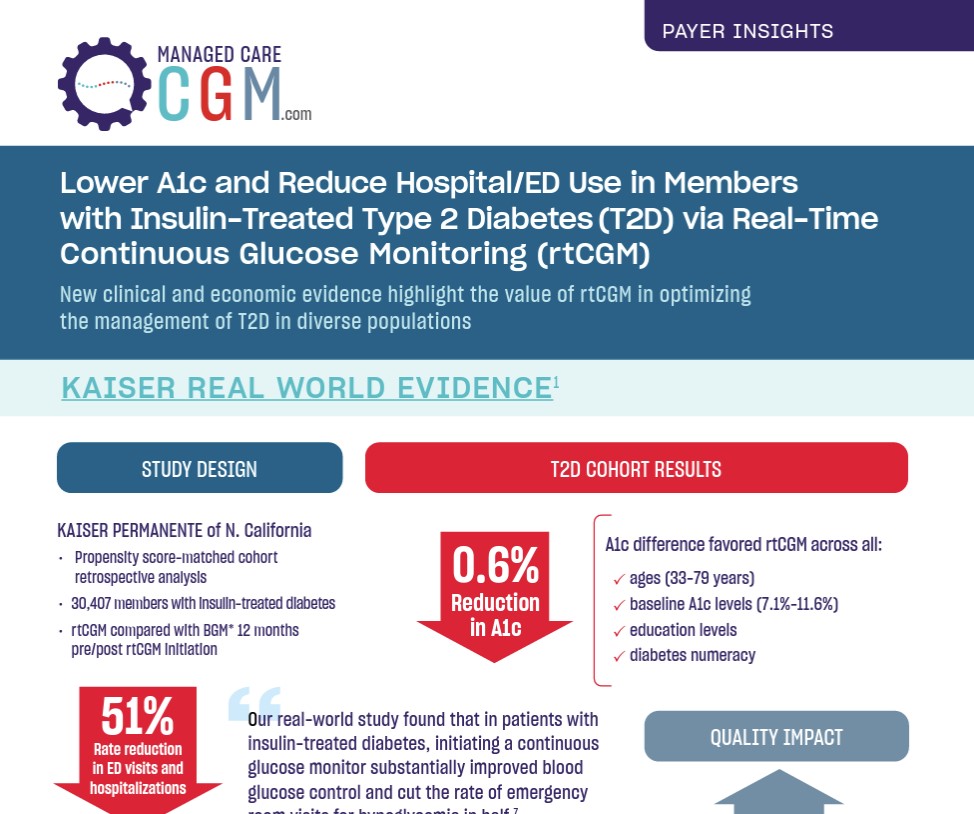


Optimize Outcomes in Insulin-Treated T1 and T2D via Evidence-Based Coverage Criteria with Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring
September 16, 2021Clinical Outcomes Coverage and Benefit Design Economic Outcomes Infographic



Association Between Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitor Use and Diabetes-Related Medical Costs for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
September 2, 2021Clinical Outcomes Economic Outcomes Article / PublicationLearn More
Sign Up To Stay Current On The Latest Coverage
Updates, Recent News, And Resources


Optimize Outcomes in Insulin-Treated T1 and T2D via Evidence-Based Coverage Criteria with Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring
September 16, 2021
Clinical Outcomes
Coverage and Benefit Design
Economic Outcomes
Infographic
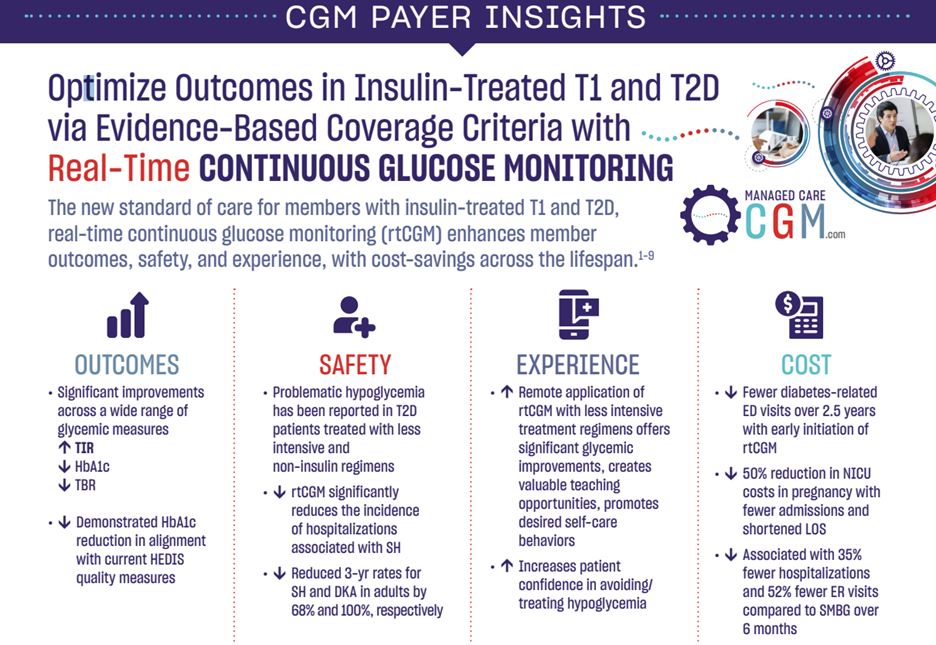


Association Between Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitor Use and Diabetes-Related Medical Costs for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
September 2, 2021Clinical Outcomes Economic Outcomes Article / PublicationLearn More


Association Between Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitor Use and Diabetes-Related Medical Costs for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
September 2, 2021
Clinical Outcomes
Economic Outcomes
Article / Publication
