Article / Publication

Source: The Journal of the American Medical Association
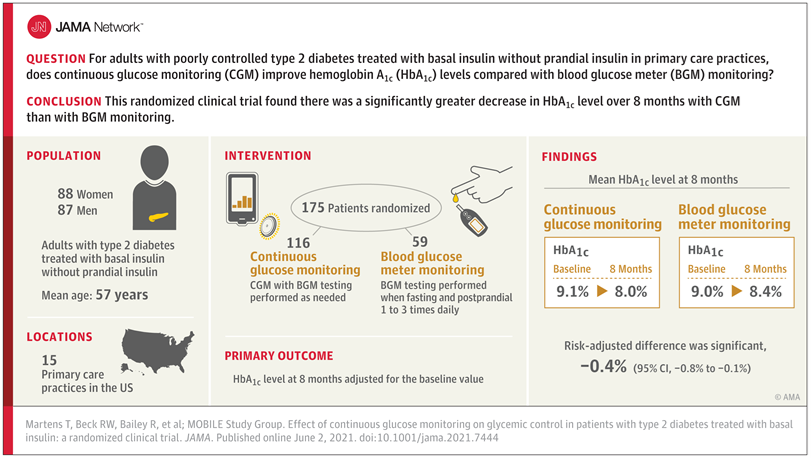
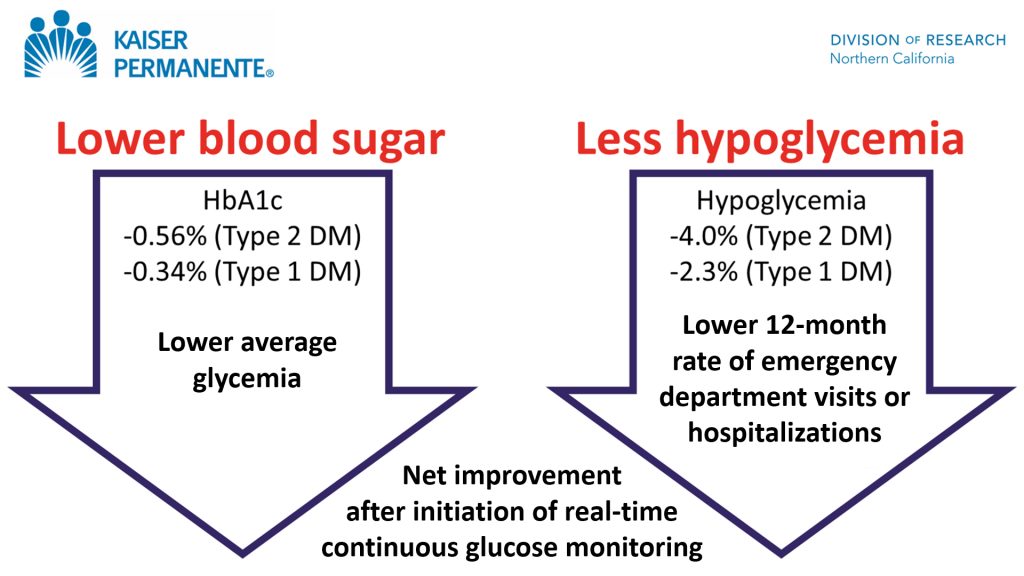
Key Takeaways: Continuous Glucose Monitoring improved outcomes more than intermittent testing of blood glucose in 41,753 patients with insulin-treated diabetes.
“Our real-world study found that in patients with insulin-treated diabetes, initiating a continuous glucose monitor substantially improved blood glucose control and cut the rate of emergency room visits for hypoglycemia in half.”1
Andrew J. Karter, PhD, Senior Research Scientist at Kaiser Permanente Division of Research
1Shaffer R. Real-time CGM lowers HbA1c, reduces ED visits in insulin-treated diabetes. Endocrine Today. June 2021. https://www.healio.com/news/endocrinology/20210607/realtime-cgm-lowers-hba1c-reduces-ed-visits-in-insulintreated-diabetes. Accessed June 24, 2021.
Learn MoreSource: The Journal of the American Medical Association
Authors: Monica E. Peek, MD, MPH, MS; Celeste C. Thomas, MD, MS
“…the studies by Karter et al. and Martens et al. provide additional evidence that patients with type 2 diabetes benefit from the use of CGM in terms of improved HbA1c level, time spent in the target blood glucose range, and reduced hypoglycemic episodes…”
“…institutional changes that promote its use in primary care will go a long way to improving diabetes control and reducing complications, particularly among the populations most in need. The time has come to broaden access to CGM for patients with type 2 diabetes.”
Learn More

Source: The Lancet – June 2021
Key Takeaways:
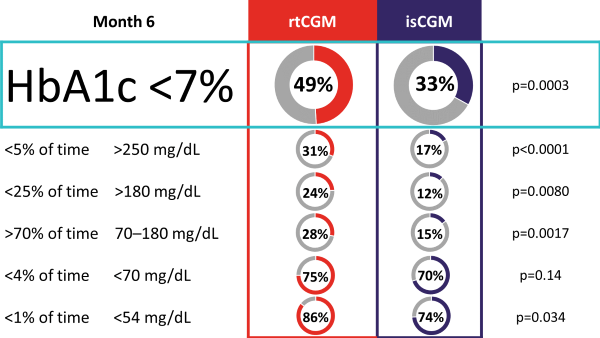
The ALERTT1 trial is the first 6-month, multicenter, prospective, randomized controlled trial comparing rtCGM with isCGM in 254 adults with type 1 diabetes, who previously used isCGM. Mean HbA1c was 7·4% (58 mmol/mol) and a minority of the study population was hypoglycemia unaware (44 [17%] people) or had a history of severe hypoglycemia (29 [11%]). Most (205 [81%]) were treated with multiple daily injections. Findings showed that in an unselected group of people with type 1 diabetes, 6-month use of rtCGM with alert functionality improved time in range (70–180 mg/dL [3.9–10.0 mmol/L]), while HbA1c, time in clinically significant hypoglycemia (< 54 mg/dL [3.0 mmol/L), and hyperglycemia (180 mg/dL [10.0 mmol/L]) were reduced. Additionally, more people on rtCGM achieved glycemic targets as defined by international consensus guidelines, and had less frequently severe hypoglycemia. Moreover, rtCGM users experienced less hypoglycemia worry and higher treatment satisfaction at the end of study.
Percentage of Participants Achieving Consensus Targets
Source: Diabetes Technology and Therapeutics
Key Takeaway: The CONCEPTT (CGM in pregnant women with type 1 diabetes) trial provided high-quality, randomized-controlled trial data demonstrating that the use of real-time CGM was associated with lower HbA1c at 34 weeks, suggesting improved maternal glucose levels during the late second and early third trimesters. Importantly, this was accompanied by 7% higher time in range (TIR) and 5% lower time above range (TAR) without increasing maternal hypoglycemia. Beyond impacting surrogate markers of maternal glycemia, using CGM led to clinically significant reductions in large for gestational-age infants, neonatal hypoglycemia, and neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) admissions.1 A systematic review combining data from CONCEPTT with that of the type 1 diabetes arm of the GlucoMOMS trial also showed evidence for a reduction in preeclampsia.
Learn MoreSource: Diabetes Technology and Therapeutics
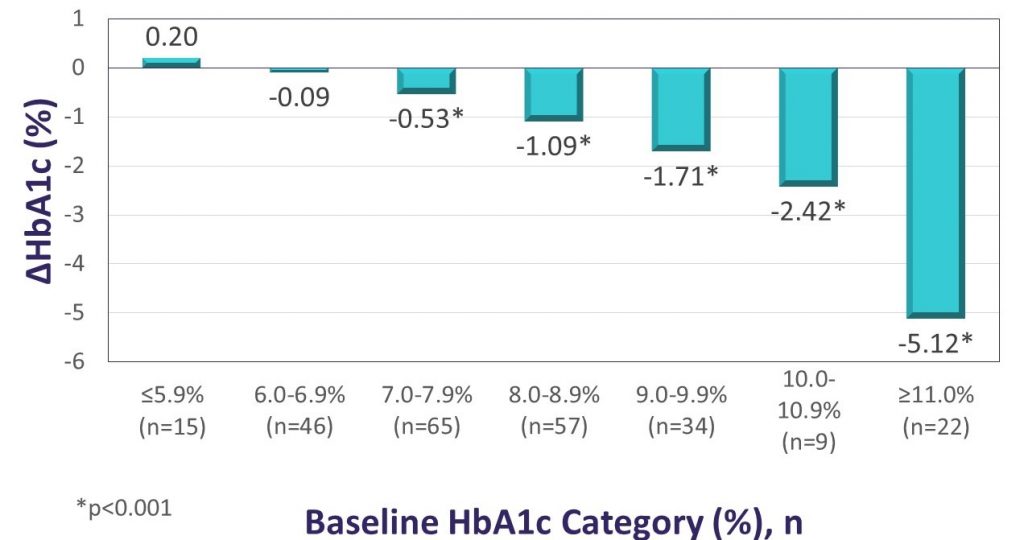
Key Takeaway: The Landmark study demonstrated significant glycemic and QoL benefits for first time CGM use among individuals using intensive insulin therapy to manage either T1D or T2D. After approximately 12 weeks of Dexcom G6 use, participants had a mean absolute reduction in HbA1c levels of 1.1%, and more than half of those with initial HbA1c values >7% experienced absolute HbA1c reductions of >1%. The reduction in HbA1c observed in Landmark was similar for patients with T1D and T2D and was more pronounced for participants with higher baseline HbA1c, consistent with observations from the DIAMOND randomized controlled trial. Significant reductions in diabetes distress and hypoglycemic concerns were also observed. In the Landmark study, there was no standardized training or intervention at CGM initiation, suggesting that the glycemic benefits can be realized without formal instruction.
Changes in HbA1c according to baseline HbA1c level
Learn More
Source: Association of Diabetes Care & Education Specialists and American Pharmacists Association
Key Takeaway: Developed by the Association for Diabetes Care and Education Specialists in partnership with APhA, this newly created Personal Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Implementation Playbook will help you implement a personal CGM program within your pharmacy practice.
This guide brings together fragmented information available from multiple sources to provide an inclusive and unbiased approach to implementation of Personal CGM into your practice, whatever its size. It includes a step-by-step approach to implementation, additional resources, and the latest research.
Download this free guide and start the process of incorporating this potentially game-changing tool for your patients living with diabetes.



Source: Association of Diabetes Care & Education Specialists and American Association of Nurse Practitioners
Key Takeaway: This toolkit provided by ADCES and AANP will help you implement a professional CGM program within your health system. Implementing a program within a healthcare setting offers many advantages, including: promotion of self-motivated, data-driven behavior change and improved clinical outcomes through alignment of medication with behavior change, resulting in lowered long-term healthcare costs for people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes.


Source: Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics
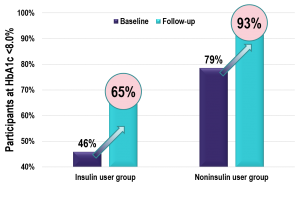
Key Takeaway: The role of real-time continuous glucose monitoring (rtCGM) is an essential component of telemedicine visits for people with diabetes. This observational study demonstrated that people with type 2 diabetes (T2D) participating in a virtual diabetes clinic can successfully insert and use Dexcom rtCGM without in-office training. The use of rtCGM was associated with a significant improvement in HbA1c at 10 months in those not meeting the ADA treatment target, independent of insulin use. In addition, there was a large shift in the percentage of participants meeting the HEDIS HbA1c target of <8.0% at follow-up; this may have important clinical and economic implications.
Chart: Percentage of Participants Achieving HEDIS HbA1c Treatment Target (HbA1c <8.0%) Before and After rtCGM Use
Source:
Key Takeaway: The intended place in therapy is as an alternative to routine blood glucose monitoring in people (over 2 years old), including pregnant women, with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, who use multiple daily insulin injections or use insulin pumps and are self-managing their diabetes. Dexcom G6 could reduce costs and would benefit the healthcare system by improving long-term outcomes, reducing the need for intensive treatment and, in the short term, reducing severe hypoglycaemic events leading to hospital admissions. Remote care may reduce the need for hospital visits.
Learn More