Article / Publication
In a retrospective claims analysis from Kaiser Permanente of Northern California, 149 patients with insulin-treated type 2 diabetes (T2D; baseline HbA1c <8%) who initiated real-time continuous glucose monitoring (RT-CGM) demonstrated durable glycemic benefit compared with 17,273 noninitiators serving as reference. RT-CGM initiation was associated with decreased HbA1c (-0.06%) while noninitiation was associated with increased HbA1c (+0.32%). A weighted adjusted difference-in-difference model of change in HbA1c yielded a net benefit of -0.30% (P=0.004) for RT-CGM. These findings highlight the notion that RT-CGM may be useful in preventing glycemic deterioration and offer a durable benefit in well-controlled patients with insulin-treated T2D.
Karter AJ, Parker MM, Moffet HH, Gilliam LK, Dlott R. Continuous Glucose Monitor Use Prevents Glycemic Deterioration in Insulin-Treated Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2022;24(5):332-337.
Learn More
In 2021, NCQA and HL7 hosted the fifth annual Digital Quality Summit (DQS) that convened stakeholders within six distinct “tracks” – each track exploring a different subset of healthcare. Track 6 of the Digital Quality Summit featured five breakout sessions that covered topics such as Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM), diabetes distress, digital measurement and measure concepts related to diabetes care, optimal care for individuals with type 1 and type 2 diabetes, NCQA’s own Diabetes Recognition Program, and more.
The Rethinking Diabetes Care in the Digital Age white paper contains findings from track 6 of the Digital Quality Summit and is broken down into the following sections:
1. Importance of Measurement in Diabetes Care beyond HbA1c and Depression
2. Optimal Diabetes Care Management and Continuous Glucose Monitoring
3. Behavioral Aspects in Diabetes Care and Diabetes Distress
4. Health Equity in Diabetes Care Management
5. Driving Improvements in Diabetes Care and the Diabetes Recognition Program
Learn More
Source: Endocrine Today
“Our real-world study found that in patients with insulin-treated diabetes, initiating a continuous glucose monitor substantially improved blood glucose control and cut the rate of emergency room visits for hypoglycemia in half,”
Andre J . Karter, PhD
Learn More

Source: Digital Technology and Therapeutics
Key Takeaway: A retrospective analysis of administrative claims data from the Optum Research Database showed rtCGM use was associated with diabetes-related medical cost reductions in patients with T2D. Increased access to rtCGM for patients with T2D may help to reduce diabetes-related cost of care.
Diabetes-related Medical Care Costs Decreased $424 PPPM After Initiating rtCGM Treatment
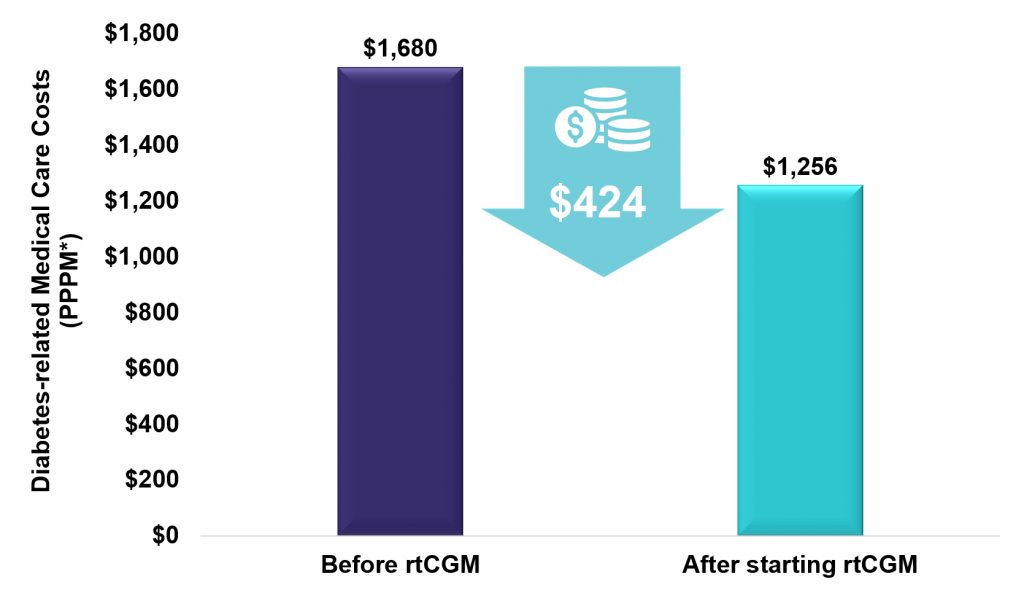
*PPPM = per patient per month
Learn More